Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 24, 2022; 13(7): 641-651
Published online Jul 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.641
Published online Jul 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.641
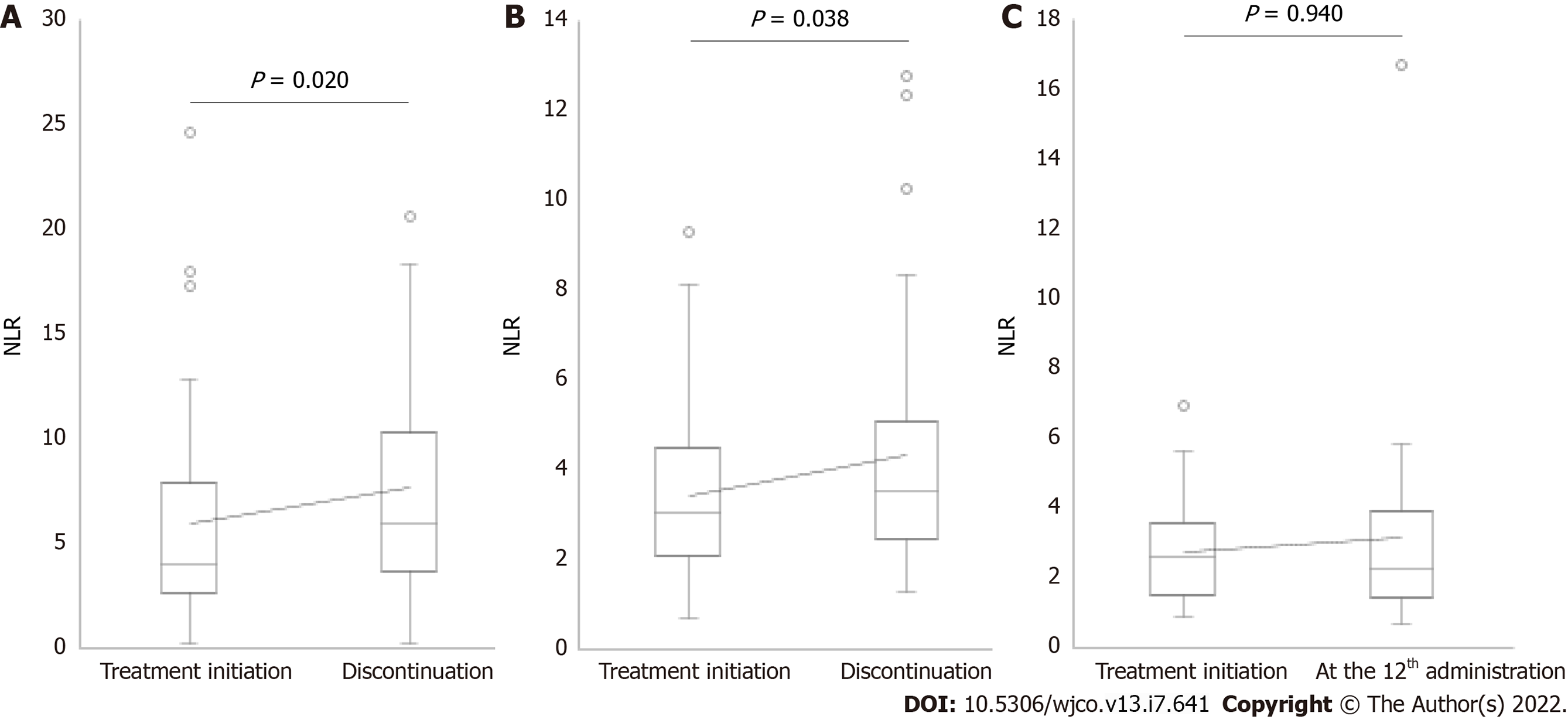
Figure 1 Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio fluctuation in patients who discontinued treatment after administering nivolumab < 6 times, who discontinued treatment after administering nivolumab 6-11 times, and who administered nivolumab ≥ 12 times.
A: A significant increase in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) was observed at the discontinuation (n = 40, median NLR = 4.01 vs 5.92, P = 0.020); B: A significant increase in NLR was observed at the discontinuation (n = 32, median NLR = 3.03 vs 3.50, P = 0.038); C: No significant difference in NLR was observed between treatment initiation and the 12th administration (n = 32, median NLR = 2.64 vs 2.32, P = 0.940). NLR: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
- Citation: Gannichida A, Nakazawa Y, Kageyama A, Utsumi H, Kuwano K, Kawakubo T. Necessity of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio monitoring for hypothyroidism using nivolumab in patients with cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2022; 13(7): 641-651
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v13/i7/641.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.641