Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 24, 2022; 13(7): 609-615
Published online Jul 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.609
Published online Jul 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.609
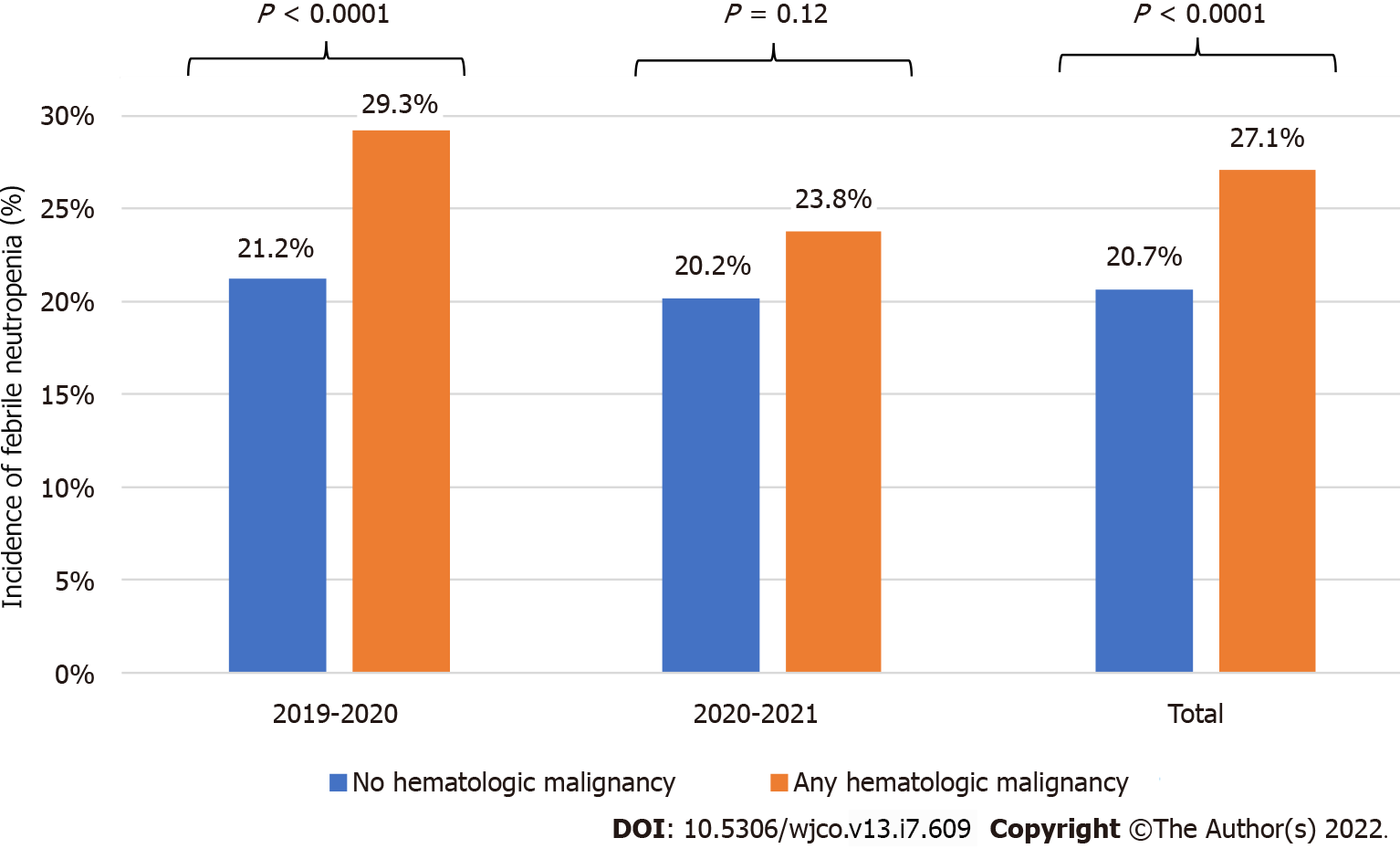
Figure 1 Incidence of febrile neutropenia in patients with an associated diagnosis of hematologic malignancy compared to those without a diagnosis of hematologic malignancy.
Patients with a diagnosis of a hematologic malignancy were significantly more likely to be febrile than those without a diagnosis of hematologic malignancy in Year 0 (21.2% vs 29.3%, P < 0.0001). This difference was not seen after implementation of public health guidelines in Year 1 (20.2% vs 23.8%, P = 0.12).
- Citation: Baracy Jr MG, Hagglund K, Kulkarni S, Afzal F, Arends K, Morris RT, Solomon LA, Aslam MF, Corey L. Decreased incidence of febrile neutropenia in Michigan following masking and social distancing orders for the COVID-19 pandemic: A population based cohort study. World J Clin Oncol 2022; 13(7): 609-615
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v13/i7/609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.609