Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 24, 2022; 13(7): 553-566
Published online Jul 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.553
Published online Jul 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.553
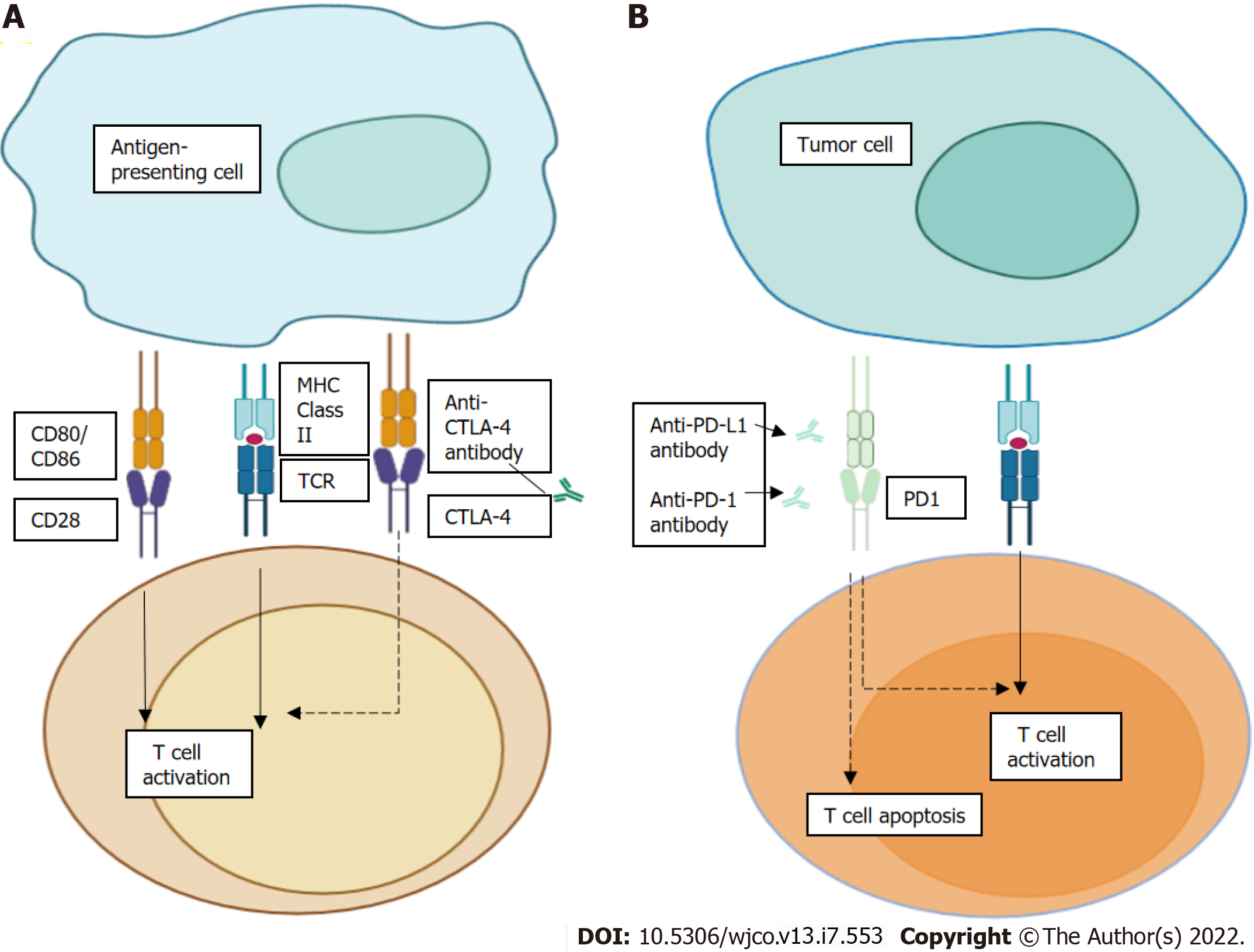
Figure 1 Mechanism of action of immune checkpoints and immune checkpoint inhibitors.
A: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitors block CTLA-4-CD80 or CTLA-4-CD86 binding to facilitate T cell activation; B: We see PD-1 as a surface receptor that is expressed by T cells and promotes apoptosis of antigen-specific T cells and reduces apoptosis of regulatory T cells through its interaction with its ligand, PD-L1, which is expressed by tumour cells and myeloid cells. CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; PD1: Programmed cell death protein 1.
- Citation: Nteli P, Bajwa DE, Politakis D, Michalopoulos C, Kefala-Narin A, Efstathopoulos EP, Gazouli M. Nanomedicine approaches for treatment of hematologic and oncologic malignancies. World J Clin Oncol 2022; 13(7): 553-566
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v13/i7/553.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i7.553