Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Oncol. May 24, 2021; 12(5): 342-354
Published online May 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i5.342
Published online May 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i5.342
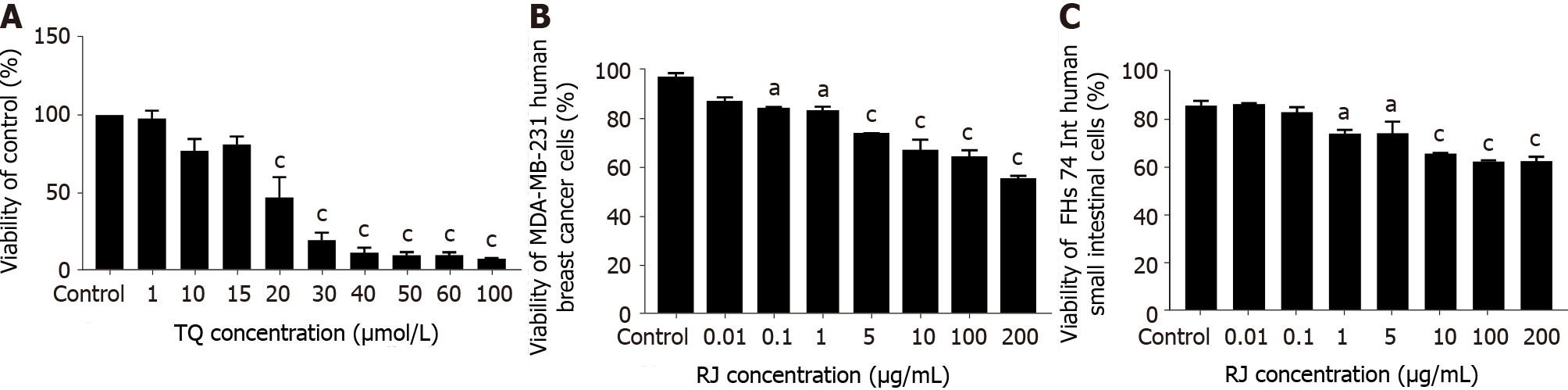
Figure 1 The inhibitory effect of thymoquinone and royal jelly on the viability of MDA-MB-231 and FHs74 Int cell line.
A: 3-(4,5-dmethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay showing the percentage viability of MDA-MB-231 cell line and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration of thymoquinone (TQ) on MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line after 24 h of treatment with different TQ concentrations. Cell viability was estimated by measuring the absorbance of the cell suspension after incubation with 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; B: Trypan blue exclusion assay showing the percentage cell viability after 24 h of treatment with different royal jelly concentrations on FHs74 Int; C: MDA-MB-231 cell lines. Data shown are an average of 3 independent experiments for panels A and B, and 2 independent experiments for panel C, respectively, expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. Asterisks represent statistically significant results compared to the control, (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001). RJ: Royal jelly; TQ: Thymoquinone.
- Citation: Moubarak MM, Chanouha N, Abou Ibrahim N, Khalife H, Gali-Muhtasib H. Thymoquinone anticancer activity is enhanced when combined with royal jelly in human breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2021; 12(5): 342-354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v12/i5/342.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v12.i5.342