Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2021; 12(12): 1227-1243
Published online Dec 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i12.1227
Published online Dec 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i12.1227
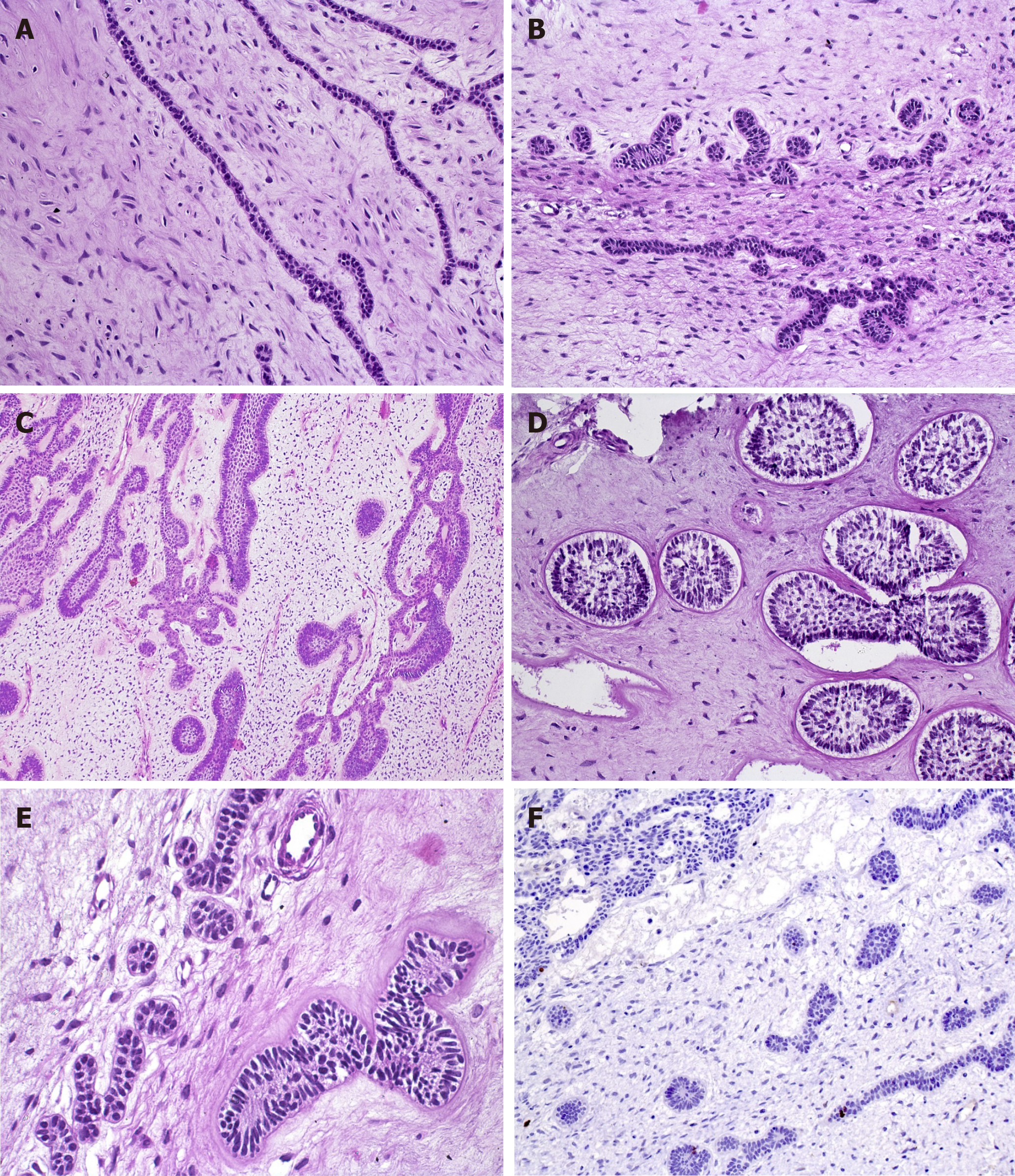
Figure 1 Diverse aspects of the odontogenic epithelium in ameloblastic fibromas within the cell-rich myxoid stroma.
A: Epithelial strands, comprising a double layer of cuboidal cells (HE, 20×); B: Epithelial proliferation with primitive appearance that resembles tooth bud-like structures (HE, 20×); C: Epithelial component with a follicular pattern comprising columnar cells at the periphery of the nests with central stellate reticulum-like cells (HE, 10×); D: Clefts of mesenchymal tissue surrounding follicular epithelial proliferations (HE, 20×); E: Mild hyalinization surrounding the basal layer of the epithelial nest (left). Smaller epithelial rosette-like islands resemble remnants of dental lamina (right) (HE, 40×); F: A very low rate of proliferation in both mesenchymal and epithelial components, showing the benign behavior of ameloblastic fibromas (IHC for Ki-67, 20×).
- Citation: Sánchez-Romero C, Paes de Almeida O, Bologna-Molina R. Mixed odontogenic tumors: A review of the clinicopathological and molecular features and changes in the WHO classification. World J Clin Oncol 2021; 12(12): 1227-1243
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v12/i12/1227.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v12.i12.1227