Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 24, 2020; 11(7): 464-476
Published online Jul 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i7.464
Published online Jul 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i7.464
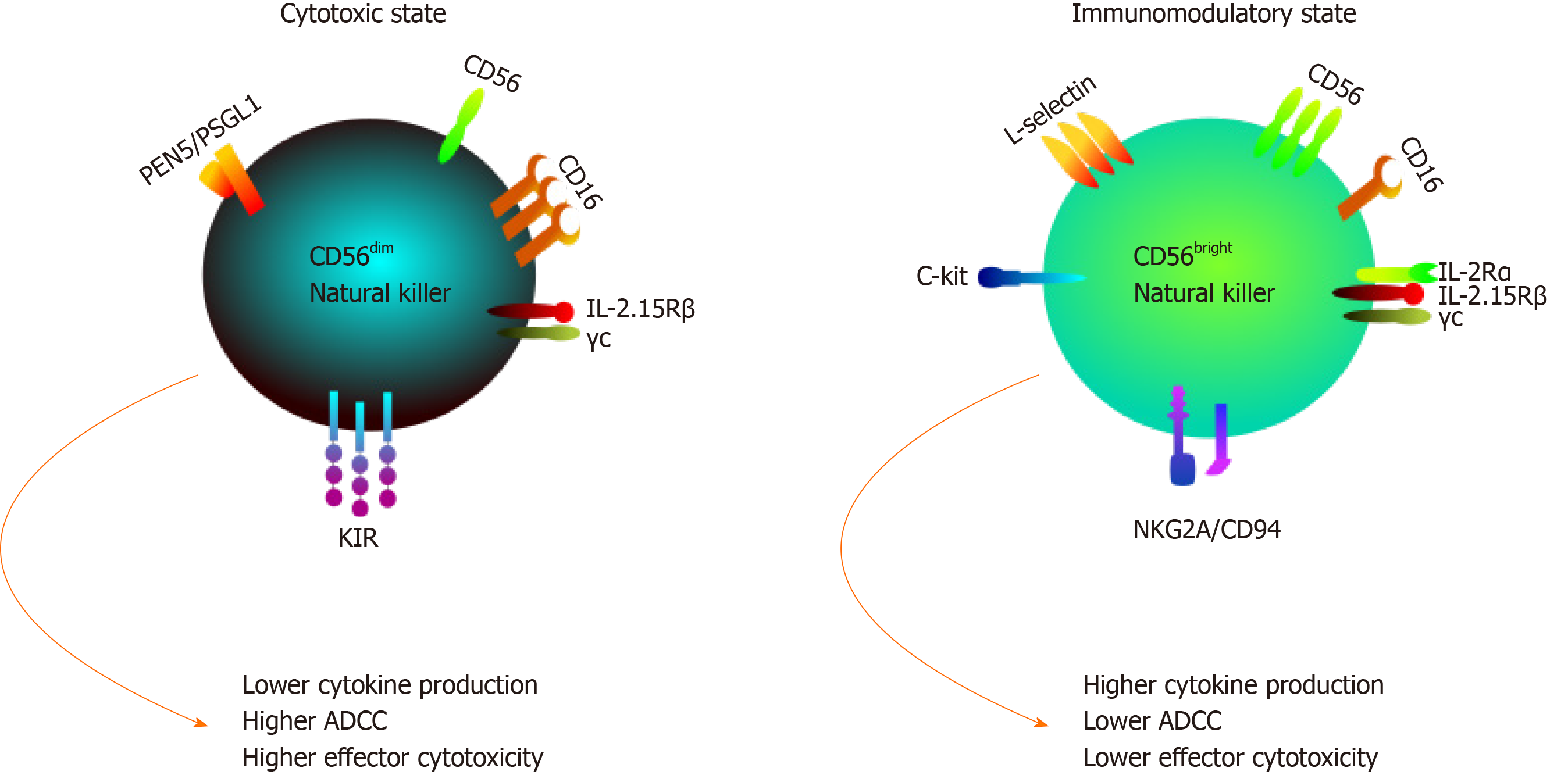
Figure 2 Natural killer cell subsets differ both functionally and phenotypically.
Functionally, CD56dim natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic cells that produce low levels of cytokines in response to monokine stimulation. Yet, they are potent mediators of cytotoxic effector functions due to high levels of CD16 surface expression. Meanwhile CD56bright NK cells are known as immunoregulatory cells that produce high levels of cytokines such as interferon-gamma, interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-β upon activation. It has low expression of CD16, thus performing reduced cytotoxic functions. Morphologically, CD56dim and CD56bright exhibit differential receptor profiles; for instance CD56dim NK cells exhibit much higher levels of killer Ig-like receptors, whereas resting CD56bright NK cells have high expression of CD94/NKG2A. ADCC: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; IL: Interleukin; KIR: Killer Ig-like receptor.
- Citation: Abdel-Latif M, Youness RA. Why natural killer cells in triple negative breast cancer? World J Clin Oncol 2020; 11(7): 464-476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v11/i7/464.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v11.i7.464