Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Oncol. May 24, 2020; 11(5): 260-274
Published online May 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i5.260
Published online May 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i5.260
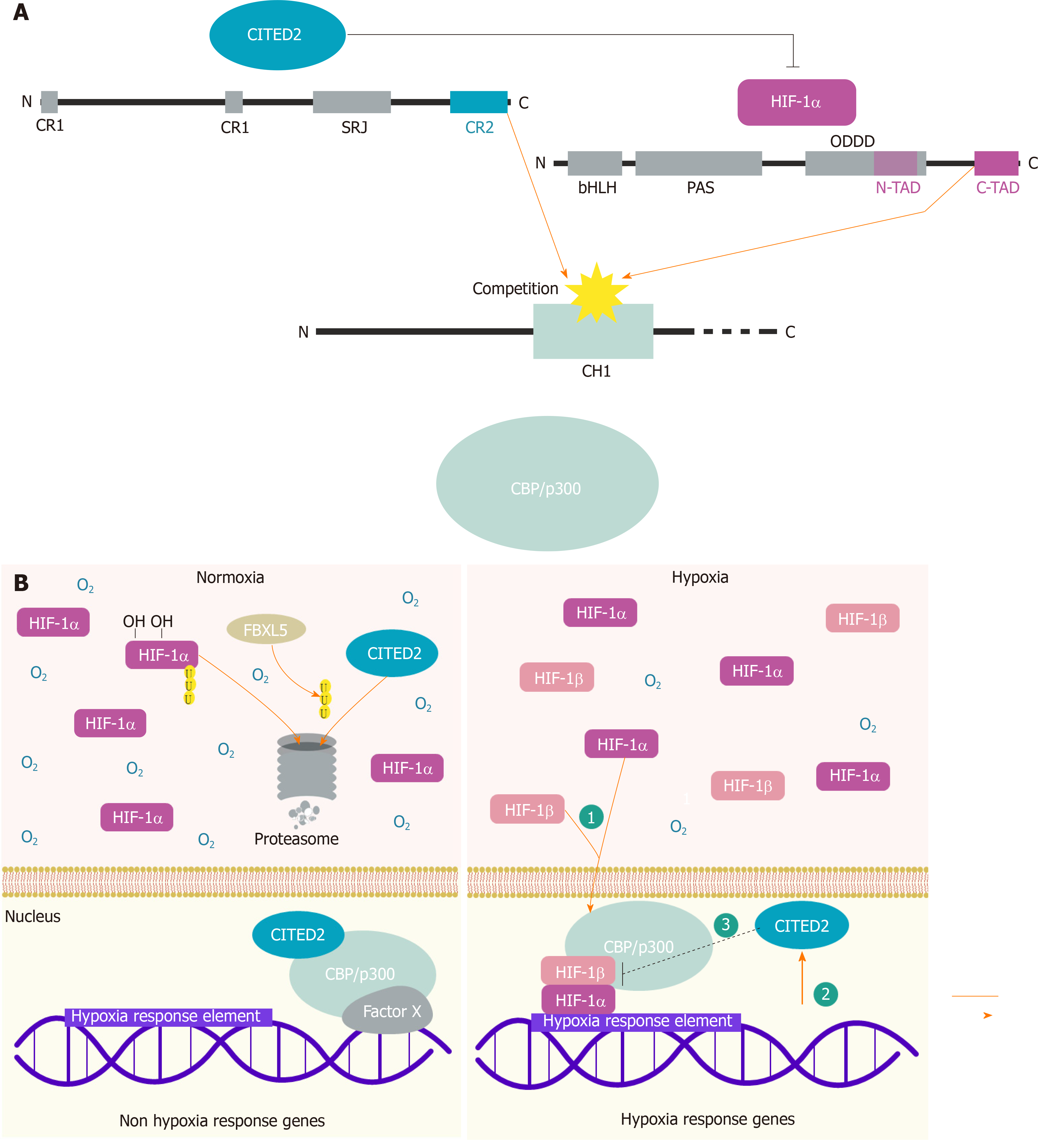
Figure 1 Structure of CITED2 and its interplay with hypoxia-inducible factors to modulate the response to hypoxia.
A: Schematic representation of CITED2, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and CBP/p300. The conserved regions amongst CITED family members, and the serine-glycine rich junction domain unique to CITED2 are indicated. Conserved regions 2 is the domain that characterizes the CITED proteins that contains a potent transactivation domain (TAD), which is responsible for the physical interaction with the domain CH1 of CBP/p300, also represented. HIF-1α has two TADs, namely, a N-terminal TAD and a C-terminal TAD, which are responsible for the transcriptional activity under hypoxia. To this end, HIF-1α binds to the CH1 region of p300, but CITED2 was shown to compete out HIF-1α for the binding to the same region, and to interfere with hypoxia-driven transcription; B: Model for CITED2, HIF-1α and CBP/p300 in hypoxia-responsive gene regulation. In normal levels of oxygen (normoxia), HIF-1α is hydroxylated at two proline residues within its oxygen-dependent degradation domain, which marks HIF-1α for proteasome degradation. In normoxia, CITED2 binds to CBP/p300 in the nucleus regulating the expression of target-gene. In addition, part of CITED2 proteins is ubiquitinated by FBXL5 and degraded by the proteasome. In hypoxia, HIF-1α is no longer hydroxylated, which prevents its degradation by the proteasome. Consequently, HIF-1α translocate and accumulates in the nucleus to associate with the HIFβ subunit to bind to specific Hypoxia-Response Elements in hypoxia-regulated genes. CITED2 competes with HIF-1α for the binding to the CH1 region of CBP/p300 and interferes with hypoxia-driven transcription. CR: Conserved regions; SRJ: Serine-glycine rich junction; TAD: Transactivation domain; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor; NAD: N-terminal TAD; CAD: C-terminal TAD.
- Citation: Fernandes MT, Calado SM, Mendes-Silva L, Bragança J. CITED2 and the modulation of the hypoxic response in cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2020; 11(5): 260-274
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v11/i5/260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v11.i5.260