Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 24, 2019; 10(6): 222-233
Published online Jun 24, 2019. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v10.i6.222
Published online Jun 24, 2019. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v10.i6.222
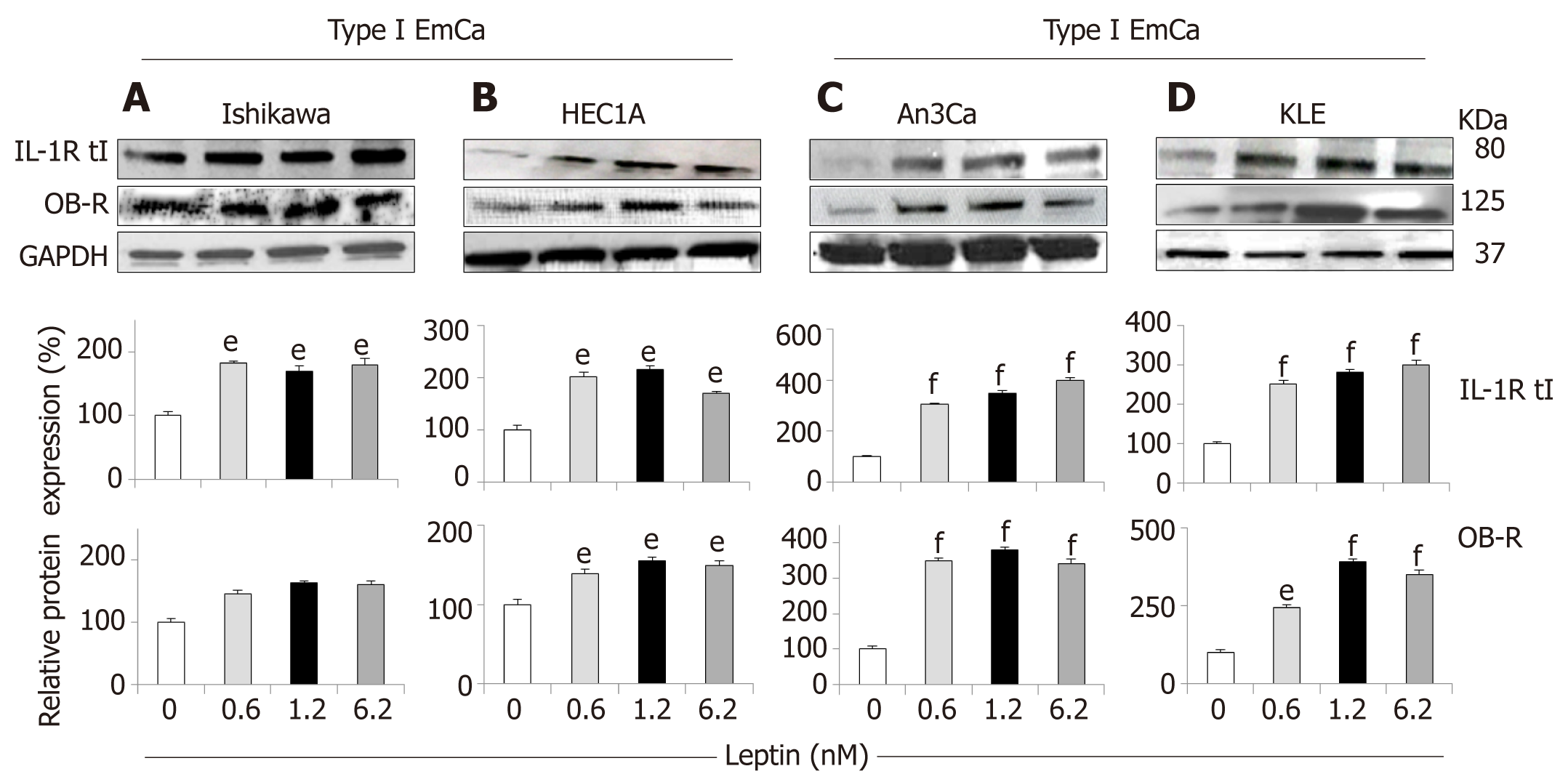
Figure 3 Leptin-induced IL-1R tI and OB-R protein expression in endometrial cancer cells.
A-D: Representative results from Western Blot (WB) analysis of leptin dose-response effects on levels of IL-1R tI and OB-R proteins in A and B [type I endometrial cancer (EmCa) cells] and B and C (type II EmCa cells). Leptin increases IL-1R tI and OB-R protein levels in type I EmCa (A, Ishikawa and B, HEC1A) and type II EmCa cells (C, An3Ca and D, KLE). Cells were cultured for 24h with leptin (0, 0.6, 1.2 and 6.2nM). Quantitative WB data (relative protein expression %) were calculated from densitometric analysis of bands with the NIH image program. The values were normalized to GAPDH as protein loading control. Data (mean ± SE) are representative of the results derived from a minimum of three independent experiments. eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs basal (no leptin).
- Citation: Daley-Brown D, Harbuzariu A, Kurian AA, Oprea-Ilies G, Gonzalez-Perez RR. Leptin-induced Notch and IL-1 signaling crosstalk in endometrial adenocarcinoma is associated with invasiveness and chemoresistance. World J Clin Oncol 2019; 10(6): 222-233
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v10/i6/222.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v10.i6.222