Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 24, 2019; 10(6): 222-233
Published online Jun 24, 2019. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v10.i6.222
Published online Jun 24, 2019. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v10.i6.222
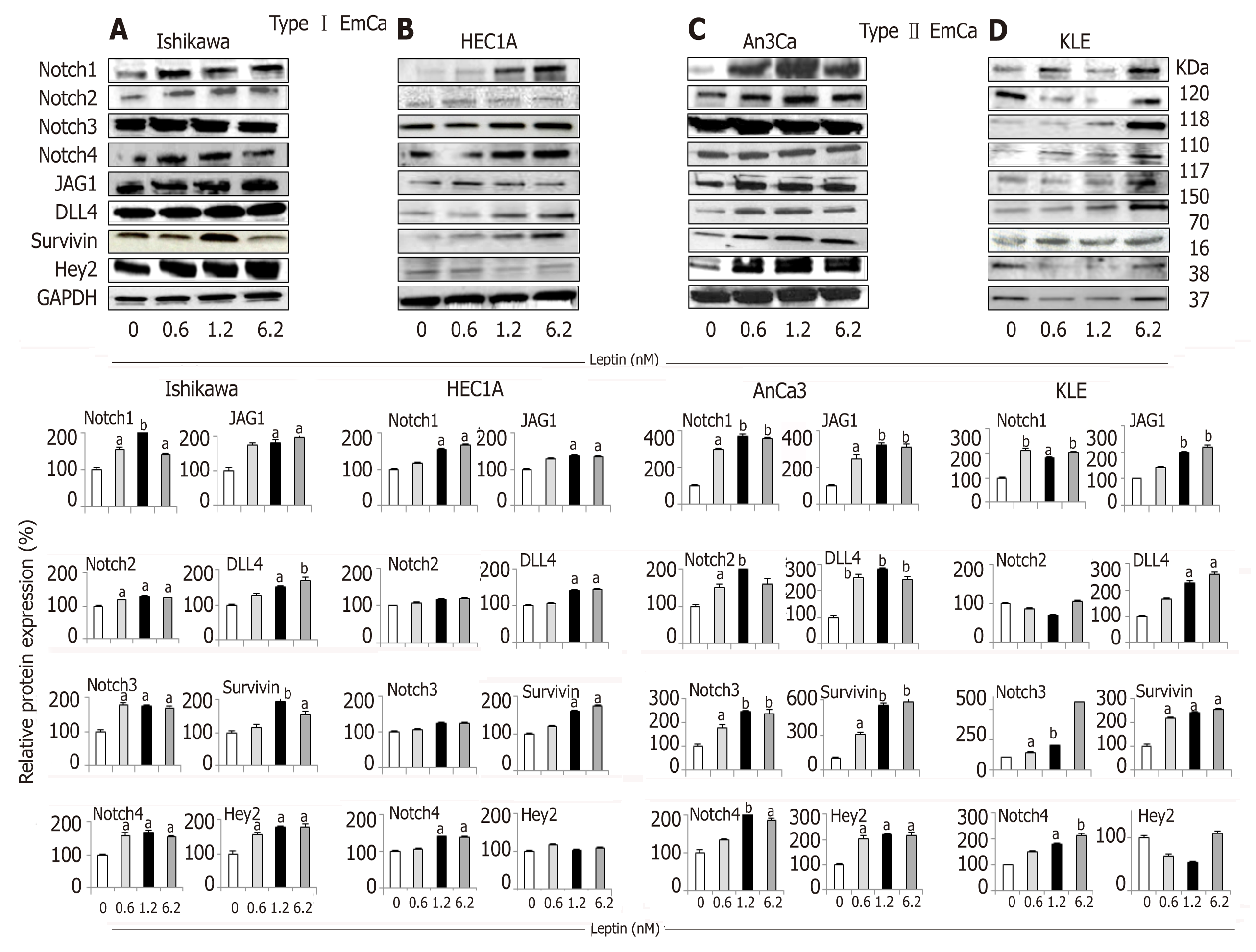
Figure 1 Leptin-induced Notch protein expression in endometrial cancer cells.
A-D: Representative results from Western Blot (WB) analysis of leptin dose-response effects on levels of Notch proteins in A and B [type I endometrial cancer (EmCa) cells] and B and C (type II EmCa cells). Leptin increases Notch protein levels (receptors: Notch1, Notch2, Notch3 and Notch4; ligands: JAG1 and DLL4 and targets: Survivin, Hey2) in type I EmCa (A, Ishikawa and B, HEC1A) and type II EmCa cells (C, An3Ca and D, KLE); Cells were cultured for 24h. Quantitative WB data (relative protein expression %) were calculated from densitometric analysis of bands with the NIH image program. The values were normalized to GAPDH as protein loading control. Data (mean ± SE) are representative results derived from a minimum of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs basal (no leptin).
- Citation: Daley-Brown D, Harbuzariu A, Kurian AA, Oprea-Ilies G, Gonzalez-Perez RR. Leptin-induced Notch and IL-1 signaling crosstalk in endometrial adenocarcinoma is associated with invasiveness and chemoresistance. World J Clin Oncol 2019; 10(6): 222-233
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v10/i6/222.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v10.i6.222