Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Oncol. Nov 10, 2010; 1(1): 3-11
Published online Nov 10, 2010. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v1.i1.3
Published online Nov 10, 2010. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v1.i1.3
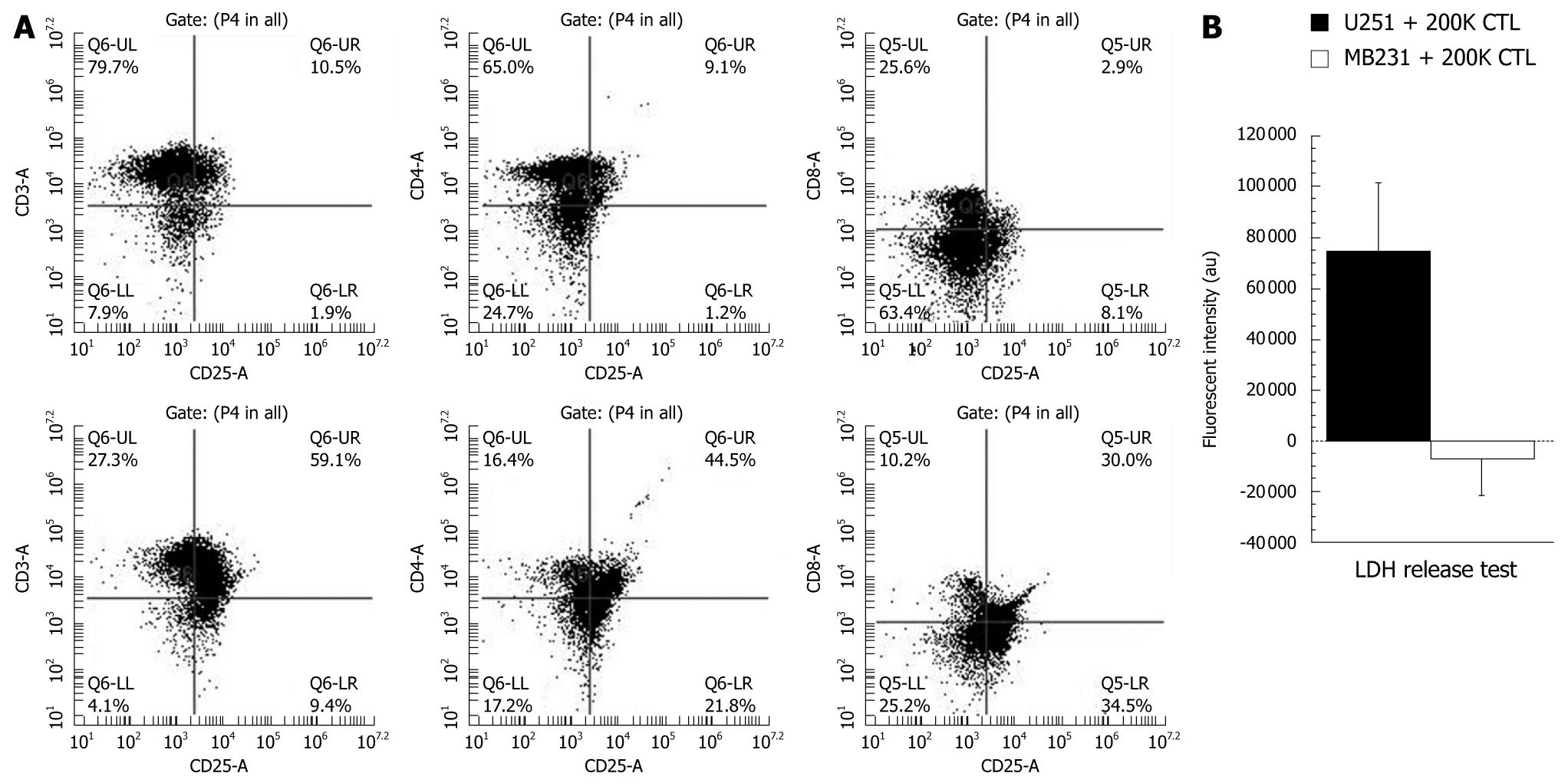
Figure 2 Phenotypic analyses of sensitized T-cells (cytotoxic T-cells) and cytotoxic activity of produced cytotoxic T-cells.
A: Analysis of T-cell markers. Phenotypic analysis of control T-cells (upper panel) and T-cells co-incubated with tumor lysate-pulsed irradiated mature dendritic cells (DCs) for 4 d (lower panel). Note the increased number of CD25+ cells (activated T-cells) after sensitizing them with DCs; B: To determine the cytotoxic specificity of the produced cytotoxic T-cells (CTLs) to U251 cells, 200 000 (200K) CTLs (sensitized to U251 cell lysate) were co-cultured overnight with U251 (100 000 cells) or human breast cancer cells (MBA-MD-231, 100 000) and the released lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was determined by a commercially available membrane integrity assay kit (Cyto Tox-ONE, Promega Corp, WI, USA). LDH levels indicate cytotoxicity since LDH is released to the media once cell membranes are damaged. Note the significantly (P≤ 0.05) increased LDH release from U251 cells indicating the specificity of produced CTLs.
- Citation: Arbab AS. Cytotoxic T-cells as imaging probes for detecting glioma. World J Clin Oncol 2010; 1(1): 3-11
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v1/i1/3.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v1.i1.3