Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Aug 6, 2016; 7(3): 406-411
Published online Aug 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i3.406
Published online Aug 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i3.406
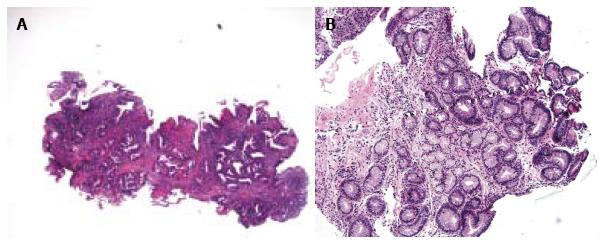
Figure 1 Examples of Barrett’s esophagus with epithelial changes, indefinite for dysplasia.
A: This esophageal biopsy shows inflamed BE with moderate architectural complexity, more extensive nuclear stratification, diminished or absent mucus production, increased cytoplasmic basophilia, resembling low-grade dysplasia, but there is presence of marked inflammation (HE stain, × 40). This biopsy is best interpreted as indefinite for dysplasia; B: This tangentially sectioned esophageal biopsy shows foci of glands with enlarged and hyperchromatic nuclei (HE stain, × 100). Because of the lack of surface epithelium as a result of tangential section, this biopsy is best interpreted as indefinite for dysplasia. BE: Barrett’s esophagus.
- Citation: Thota PN, Kistangari G, Esnakula AK, Gonzalo DH, Liu XL. Clinical significance and management of Barrett’s esophagus with epithelial changes indefinite for dysplasia. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2016; 7(3): 406-411
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v7/i3/406.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i3.406