Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Feb 6, 2016; 7(1): 145-155
Published online Feb 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i1.145
Published online Feb 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i1.145
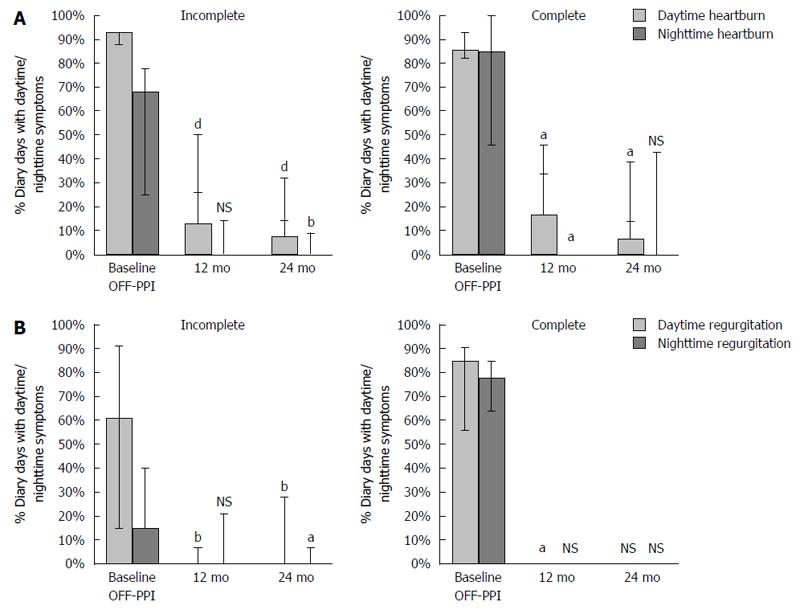
Figure 2 Frequency of daytime and nighttime symptoms of (A) heartburn and (B) regurgitation at baseline and with lower esophageal sphincter - electrical stimulation therapy at 12 and 24 mo.
Data are presented as median and interquartile range (IQR). Absence of median value or IQR bars indicate a value of zero for the listed variables. NS = Not significant, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001. A: Percent days with Heartburn at baseline, 12- and 24-mo following LES-EST. There was a significant reduction in reported daytime and nighttime with heartburn at both time points compared to baseline, in both groups; B: Percent of days with Regurgitation at baseline, 12- and 24-mo following LES-EST. There was a marked reduction in reported daytime and nighttime with regurgitation at both time points compared to baseline, in the incomplete responder group and a marked reduction in these variables in the responder group. LES: Lower esophageal sphincter; EST: Electrical stimulation therapy.
- Citation: Soffer E, Rodríguez L, Rodriguez P, Gómez B, Neto MG, Crowell MD. Effect of electrical stimulation of the lower esophageal sphincter in gastroesophageal reflux disease patients refractory to proton pump inhibitors. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2016; 7(1): 145-155
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v7/i1/145.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i1.145