Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Nov 6, 2015; 6(4): 223-237
Published online Nov 6, 2015. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i4.223
Published online Nov 6, 2015. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i4.223
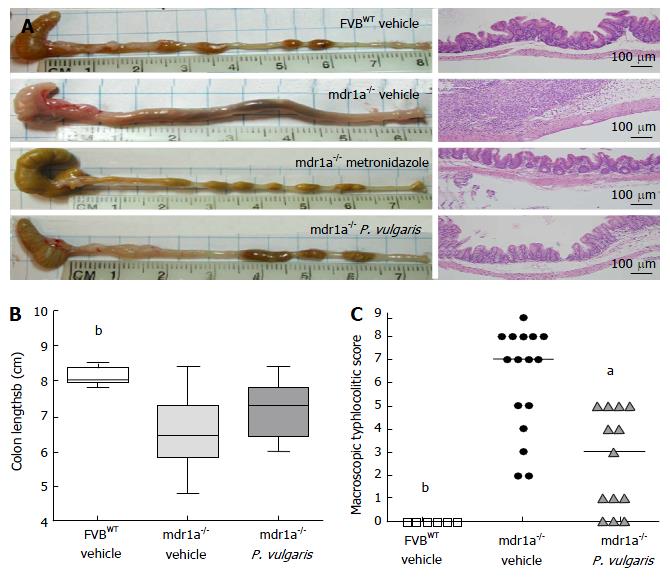
Figure 2 Oral administration of a Prunella vulgaris extract attenuated both microscopic and macroscopic cecal lesions in mdr1a-/- mice.
A: Representative photographs of ceca and colons (left) and representative photomicrographs (200 ×) of histological sections of ceca (right) collected at necropsy from FVBWT or mdr1a-/- mice treated with either vehicle or Prunella vulgaris (P. vulgaris) extract; B: Colon lengths were measured at necropsy and the group range is represented. Whiskers indicate minimum and maximum values, while the horizontal line represents the group median; C: Macroscopic typhlocolitic scores were assigned at necropsy as described in the Materials and Methods (Max/Severe = 9, Min/Healthy = 0). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 compared to mdr1a-/- vehicle as calculated by Kruskal-Wallis test. Vehicle-treated FVBWT mice n = 6, vehicle-treated mdr1a-/- mice n = 16, P. vulgaris-treated mdr1a-/- mice n = 13.
-
Citation: Haarberg KM, Wymore Brand MJ, Overstreet AMC, Hauck CC, Murphy PA, Hostetter JM, Ramer-Tait AE, Wannemuehler MJ. Orally administered extract from
Prunella vulgaris attenuates spontaneous colitis in mdr1a-/- mice. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2015; 6(4): 223-237 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v6/i4/223.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i4.223