Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Nov 6, 2014; 5(4): 209-217
Published online Nov 6, 2014. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v5.i4.209
Published online Nov 6, 2014. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v5.i4.209
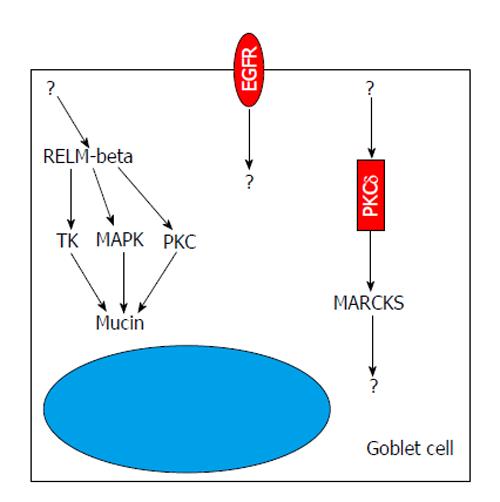
Figure 2 Intestinal Goblet cells employ different mechanisms including protein kinase related pathways to modulate the secretion of mucus, such as pathways related to tyrosine kinase, protein kinase C delta, myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate or receptors with tyrosine kinase activity such as epidermal growth factor receptor.
MARCKS: Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; TK: tyrosine kinase; RELM-beta: Resistin-like molecule beta; PKCδ: Protein kinase C delta; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase.
- Citation: Yang L, Yan Y. Protein kinases are potential targets to treat inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2014; 5(4): 209-217
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v5/i4/209.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v5.i4.209