Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Oct 6, 2011; 2(5): 42-45
Published online Oct 6, 2011. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v2.i5.42
Published online Oct 6, 2011. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v2.i5.42
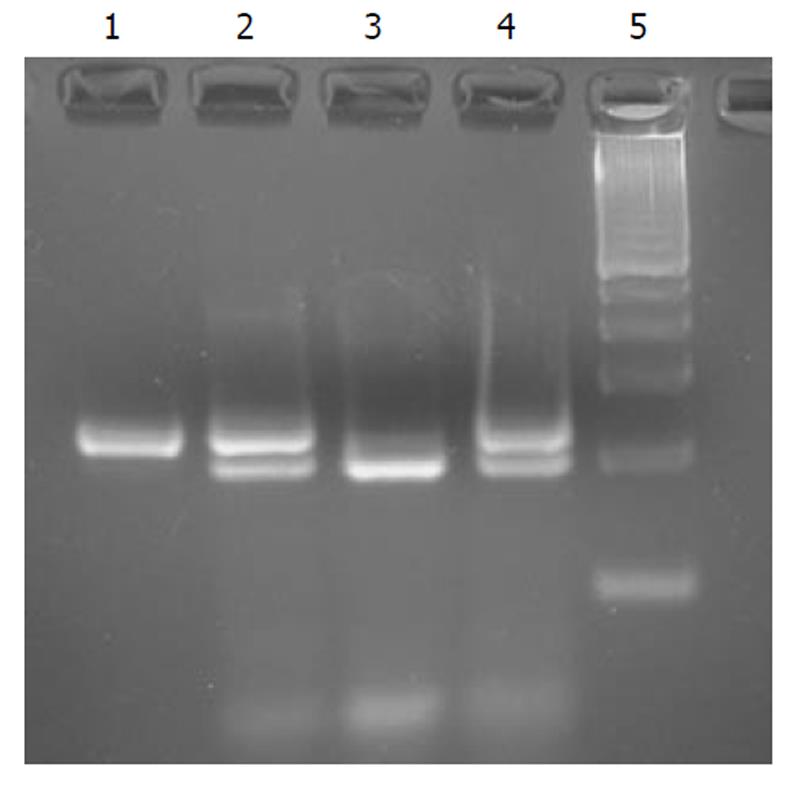
Figure 3 G71R G>A at nt +211, polymerase chain reaction-RFLPs analysis.
Electrophoresis on a 4% agarose gel of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products from exon I. Lane 1: PCR product (235 bp); lanes 2-4: PCR products digested with MspI; Lane 5: 100 bp ladder. Lane 2 shows a heterozygote for G71R mutation (proposita’s PCR product, 235 bp + 203 bp + 32 bp), Lane 3 shows a wild type for G71R mutation (mother’s PCR product, 203 bp + 32 bp), Lane 4 shows a hetorozygote for G71R mutation (father’s PCR product, 235 bp + 203 bp + 32 bp).
- Citation: Kalotychou V, Karakosta M, Tzanetea R, Stamoulakatou A, Konstantopoulos K, Rombos Y. Contribution of G71R mutation to Gilbert’s syndrome phenotype in a Greek patient: A case report. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2011; 2(5): 42-45
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v2/i5/42.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v2.i5.42