Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2017; 8(4): 150-160
Published online Nov 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i4.150
Published online Nov 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i4.150
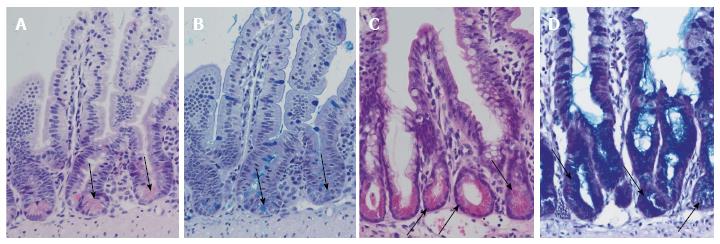
Figure 2 Differentiation of Paneth cells and Notch inhibition.
Normal ileal mouse mucosa with normal crypts and Paneth cells: HE staining (A) and alcian-PAS staining (B). Arrows indicate Paneth cells. Ileal mouse tissues after treatment with dibenzazepine show an increase in secretory cells in the crypts with differentiation of Paneth cell-like epithelia (arrows): HE staining (C) and alcian-PAS staining (D).
- Citation: Gassler N. Paneth cells in intestinal physiology and pathophysiology. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2017; 8(4): 150-160
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v8/i4/150.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v8.i4.150