Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2017; 8(3): 142-149
Published online Aug 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.142
Published online Aug 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.142
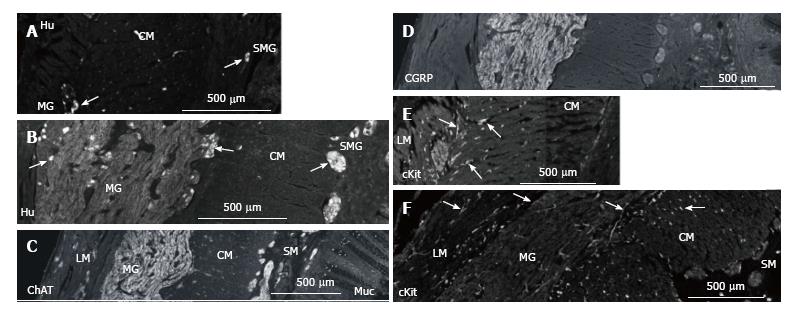
Figure 3 Nerve cells in myenteric and submucosal ganglia in normal colon and MEN2B colon.
A: Hu immunoreactivity showing nerve cell bodies in transverse colon cut with circular muscle in cross section. Control patient (HSCR) showing myenteric ganglia (MG) neurons and submucosal ganglia; B: MEN2B patient at same magnification showing greatly enlarged MG containing 41 neurons and multiple large ganglia in the submucosa (SMG) containing 2-6 neurons. Note most of the increase in size of the MG is due to nerve fibres; C: Choline acetyle transferase (ChAT) immunoreactivity in transverse colon of MEN2B patient. Note many large ganglia in the submucosa (SM); D: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunoreactivity in transverse colon of MEN2B patient. CGRP labels extrinsic sensory nerves. Note most of labelling is in the myenteric ganglia; E: ICC in the muscle in normal colon (HSCR); F: MEN2B colon. cKit-immunoreactivity shows ICC in the muscle and around the MG (arrows) and shows mast cells in the mucosa and submucosa. Mast cells are round cells with no process while ICC are elongate cells with processes. ICC numbers are similar in control and MEN2B. The longitudinal muscle (LM), myenteric ganglia (MG), circular muscle (CM), submucosa (SM), submucosal ganglia (SMG) and mucosa (Muc) are shown from left to right.
- Citation: Hutson JM, Farmer PJ, Peck CJ, Chow CW, Southwell BR. Multiple endocrine neoplasia 2B: Differential increase in enteric nerve subgroups in muscle and mucosa. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2017; 8(3): 142-149
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v8/i3/142.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.142