Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. May 15, 2017; 8(2): 67-76
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i2.67
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i2.67
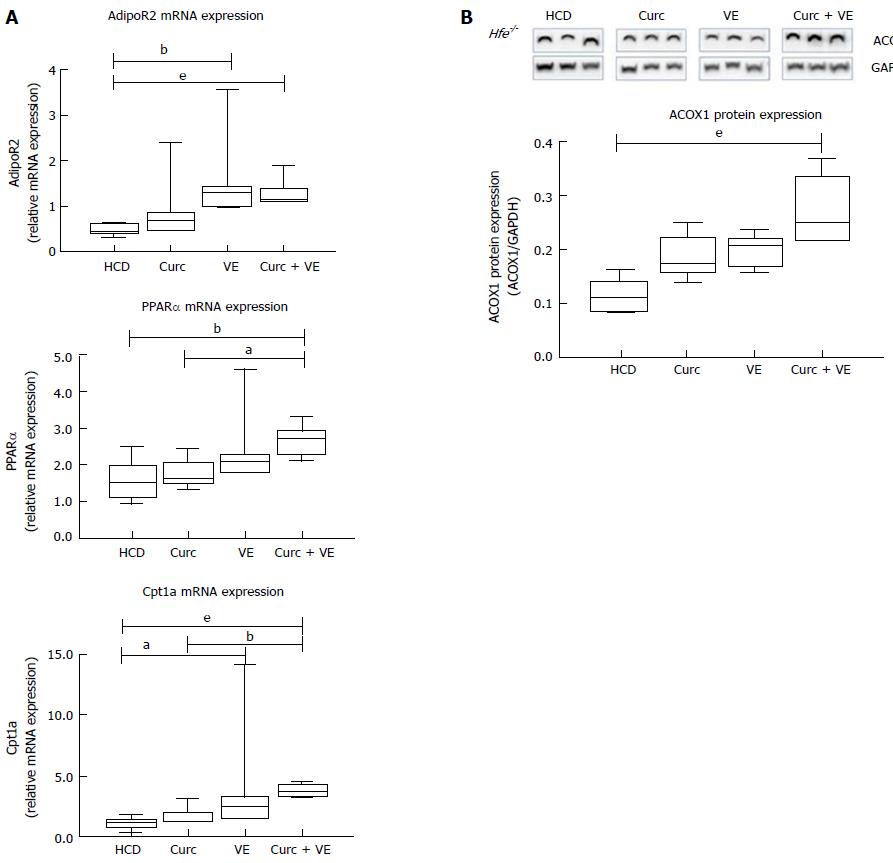
Figure 3 Altered lipid signalling following high calorie diet feeding is abrogated by curcumin and vitamin E combination therapy.
qRT-PCR was used to determine expression levels of hepatic fatty acid oxidation genes in Hfe-/- mice fed HCD, HCD + Cu, HCD + VE or HCD + Cu + VE. A: Adiponectin receptor 2 (AdipoR2) mRNA; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) and carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (Cpt1a) mRNA; B: Western blotting and densitometry analysis was performed to determine levels of acyl-coenzymeA oxidase 1 (ACOX) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh). Data are depicted using box and whisker plots showing median, minimum and maximum values. Statistical significance was tested using Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s correction for multiple comparisons, aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, eP ≤ 0.001. HCD: High calorie diet; Cu: Curcumin; VE: Vitamin E.
- Citation: Heritage M, Jaskowski L, Bridle K, Campbell C, Briskey D, Britton L, Fletcher L, Vitetta L, Subramaniam VN, Crawford D. Combination curcumin and vitamin E treatment attenuates diet-induced steatosis in Hfe-/- mice. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2017; 8(2): 67-76
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v8/i2/67.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v8.i2.67