Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. May 15, 2017; 8(2): 59-66
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i2.59
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i2.59
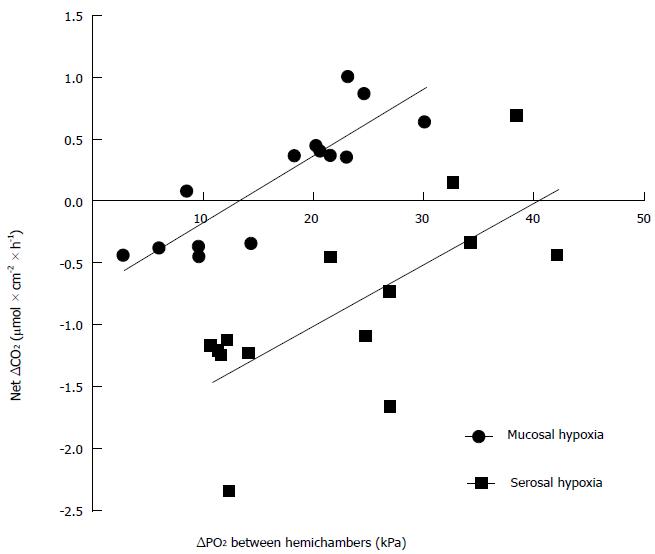
Figure 3 Rate of change in oxygen content of the hypoxic hemichamber as a function of the difference in oxygen partial pressure between hemichambers.
Various degrees of hypoxia were induced in either the serosal or the mucosal hemichamber while keeping the opposite hemichamber fully oxigenated, and the change in oxygen content was plotted as a function of the mean difference in oxygen pressure between both hemichambers during a 30-min observation period. The slope of the relationships was the same when either the serosal or the mucosal hemichamber was hypoxic (P = 0.8244), but the oxygen pressure difference at which there was no net change in oxygen content in the hypoxic hemichamber was larger when hypoxia was induced in the serosal hemichamber (P < 0.0001). ΔCO2: Change in oxygen content of the hypoxic hemichamber; ΔPO2: Oxygen pressure difference between hemichambers.
- Citation: Saraví FD, Carra GE, Matus DA, Ibáñez JE. Rectification of oxygen transfer through the rat colonic epithelium. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2017; 8(2): 59-66
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v8/i2/59.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v8.i2.59