Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2016; 7(4): 300-306
Published online Nov 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i4.300
Published online Nov 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i4.300
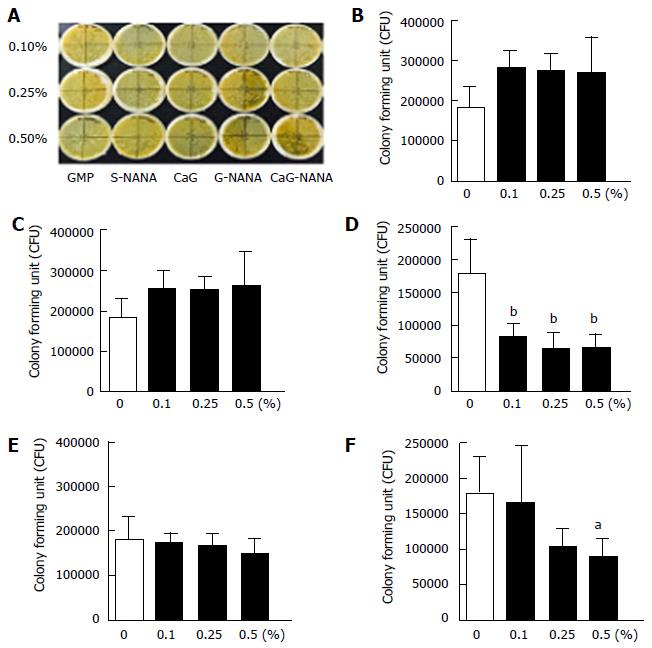
Figure 2 Inhibitory effect of calcium-glycomacropeptide-N-acetylneuraminic acid on Helicobacter pylori in vitro.
Agar plates were inoculated with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) at serial concentrations of 1 × 108, 1 × 107, and 1 × 106 CFU/mL and cultured for 72 h. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) was defined as the minimal concentration of materials required for complete inhibition of H. pylori growth. Bactericidal activity was evaluated using time-kill curves with 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 × MIC of CaG-NANA compared with blank controls. All experiments were performed three times and significance was set at aP < 0.1 and bP < 0.05. A: Picture of colony forming unit assay; B: GMP; C: CaG; D: S-NANA; E: G-NANA; F: CaG-NANA. GMP: Glycomacropeptide; CaG: Calcium-glycomacropeptide; S-NANA: Ststandard N-acetylneuraminic acid; CaG-NANA: Calcium-glycomacropeptide-N-acetylneuraminic acid.
- Citation: Rhee YH, Ku HJ, Noh HJ, Cho HH, Kim HK, Ahn JC. Anti-Helicobacter pylori effect of CaG-NANA, a new sialic acid derivative. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(4): 300-306
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i4/300.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i4.300