Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. May 15, 2016; 7(2): 223-234
Published online May 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i2.223
Published online May 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i2.223
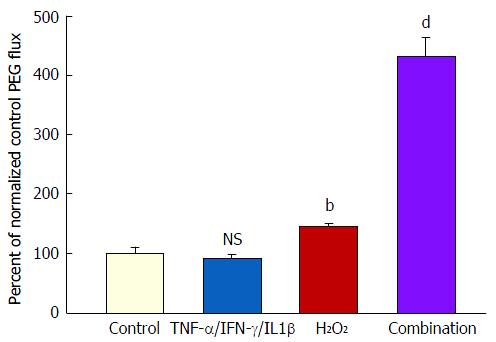
Figure 5 The effect of tumor necrosis factor-α + interferon-γ + interleukin-1β plus hydrogen peroxide on transepithelial flux of 14C-polyethylene glycol.
Seven-day and 21-d post-confluent CACO-2 cell layers on Millipore PCF filters were refed in control medium or medium containing the combination of 200 ng/mL TNF-α, 200 ng/mL IFN-γ, and 50 ng/mL IL1β (apical and basal-lateral compartments) 48 h prior to radiotracer flux studies. On the day of the experiment, the cell layers were treated for 5 h with control saline or saline containing 2 mmol/L H2O2. Paracellular permeability was assessed using 0.1 mmol/L, 0.3 μCi/mL 14C-polyethylene glycol as described in materials and methods. Data represent the percent of control flux rate normalized across 2 experiments, and is expressed as the mean ± SE for 8 cell layers per condition. NS indicates non significance vs control. bP < 0.01 vs control; dP < 0.001 vs control (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc testing). IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; IL1β: Interleukin-1β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: DiGuilio KM, Mercogliano CM, Born J, Ferraro B, To J, Mixson B, Smith A, Valenzano MC, Mullin JM. Sieving characteristics of cytokine- and peroxide-induced epithelial barrier leak: Inhibition by berberine. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(2): 223-234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i2/223.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i2.223