Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Feb 15, 2016; 7(1): 17-26
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.17
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.17
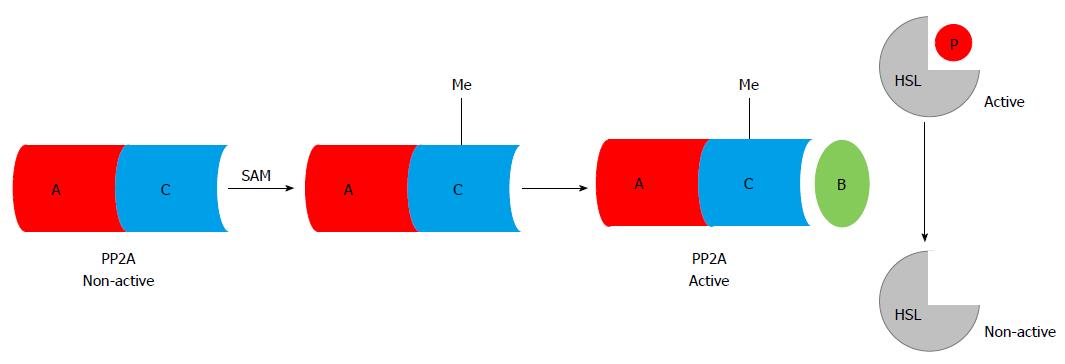
Figure 2 S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methylation reactions are required for protein phosphatase 2A activation, which dephosphorylates (inhibits) hormone sensitive lipase.
Chronic alcohol consumption induces intracellular hypomethylation status in adipocytes, which suppresses PP2A activity, leading to uncontrolled HSL activation. SAM: S-adenosylmethionine; Me: Methyl group; PP2A: Protein phosphatase 2A; HSL: Hormone sensitive lipase.
- Citation: Wang ZG, Dou XB, Zhou ZX, Song ZY. Adipose tissue-liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(1): 17-26
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i1/17.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.17