Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Feb 15, 2016; 7(1): 160-170
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.160
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.160
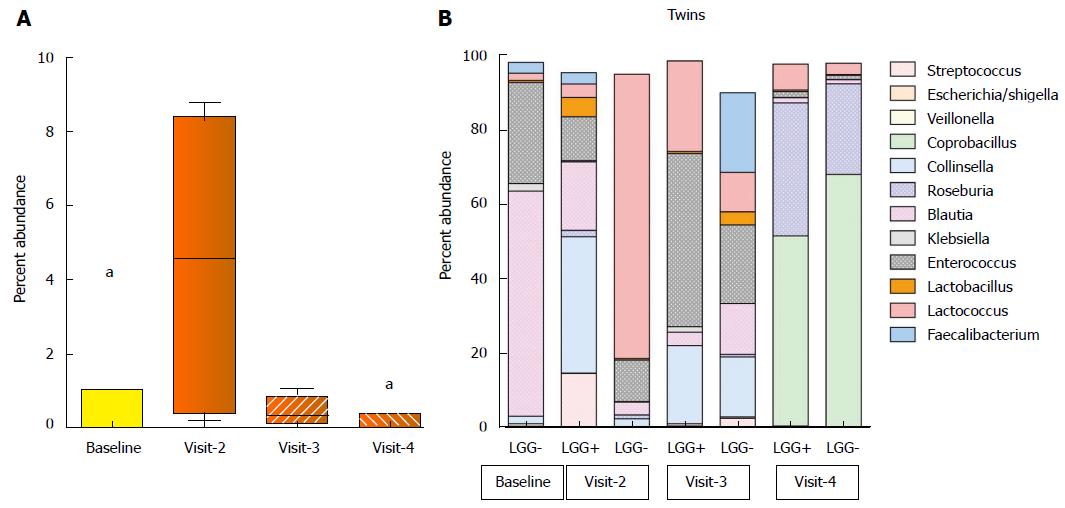
Figure 3 Abundance of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and shifts in composition of stool specimens.
A: Lactobacillus rhamnosus 16S rDNA sequence abundance in colicky infants at baseline and 14, 42 and 90 d after treatment with LGG (visits 2, 3 and 4). The median, 25th-75th percentiles (boxes) and 10th-90th percentiles (whiskers) are represented. Black dots represent outliers. aP < 0.05 compared to baseline and all other visits, respectively; B: Twins’ bacterial distribution at genus level. The abundance of major bacterial genera in stools of twin infants with colic: baseline (visit 1) and 14, 42 and 90 d after assignment to formula +/- LGG (visits 2, 3 and 4). Only one stool sample was evaluable at visit 1. The percent of abundance of Lactobacillus was indicated as orange box which was increased in LGG+ compared to LGG- at visit 2 (P < 0.05). LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.
- Citation: Fatheree NY, Liu Y, Ferris M, Van Arsdall M, McMurtry V, Zozaya M, Cai C, Rahbar MH, Hessabi M, Vu T, Wong C, Min J, Tran DQ, Navarro F, Gleason W, Gonzalez S, Rhoads JM. Hypoallergenic formula with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG for babies with colic: A pilot study of recruitment, retention, and fecal biomarkers. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(1): 160-170
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i1/160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.160