Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Feb 15, 2016; 7(1): 160-170
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.160
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.160
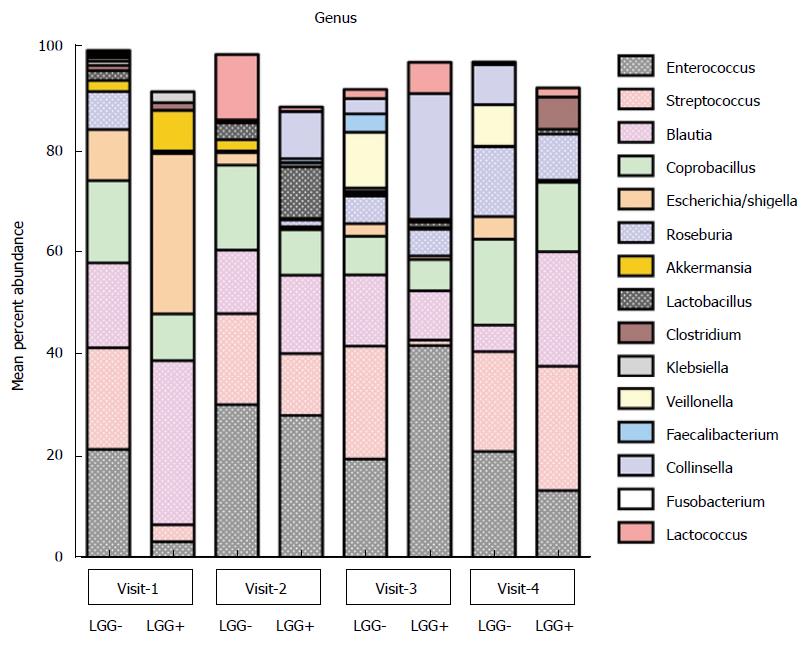
Figure 2 Fecal microbiota of infants with colic before and after treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG vs placebo.
Average percent abundance of major bacterial groups at the genus level in colicky infants treated with LGG [LGG (+), n = 3] or placebo [LGG(-), n = 6]. Note that this was the subset of infants that had stools available for analysis at each of the 4 clinic visits. Visit 1 (day 1); visit 2 (day 14); visit 3 (day 42); and visit 4 (day 90). LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.
- Citation: Fatheree NY, Liu Y, Ferris M, Van Arsdall M, McMurtry V, Zozaya M, Cai C, Rahbar MH, Hessabi M, Vu T, Wong C, Min J, Tran DQ, Navarro F, Gleason W, Gonzalez S, Rhoads JM. Hypoallergenic formula with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG for babies with colic: A pilot study of recruitment, retention, and fecal biomarkers. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(1): 160-170
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i1/160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.160