Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2014; 5(4): 496-513
Published online Nov 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.496
Published online Nov 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.496
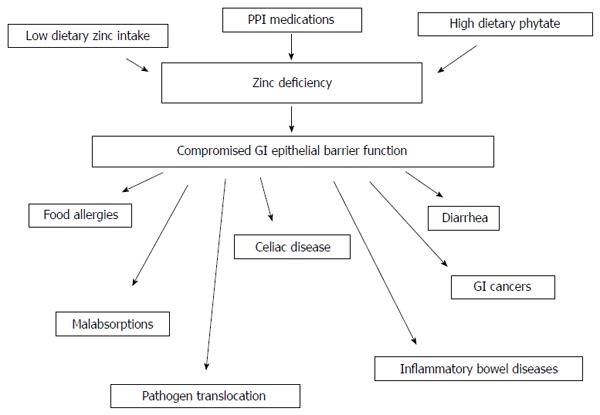
Figure 1 Zinc deficiency can arise from several sources, and a major physiological effect of zinc deficiency will be to induce leakiness in tight junctional seals and consequently epithelial cell layers.
This figure diagrammatically shows the conditions/diseases that could be promoted by this eventuality arising in the gastrointestinal mucosa; GI: Gastrointestinal; PPI: Proton pump inhibitor.
- Citation: Skrovanek S, DiGuilio K, Bailey R, Huntington W, Urbas R, Mayilvaganan B, Mercogliano G, Mullin JM. Zinc and gastrointestinal disease. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014; 5(4): 496-513
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v5/i4/496.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.496