Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2014; 5(3): 252-270
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.252
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.252
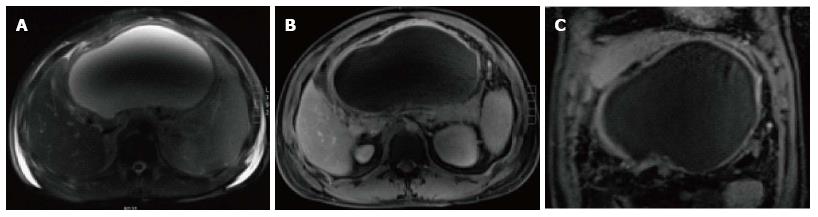
Figure 12 Large pancreatic pseudocyst.
A: Axial fast spin-echo T2- weighted image with fat-suppression; B-C: Axial and coronal post-contrast 3D- GRE T1-weighted images with fat-suppression during the portal venous phase. There is a very large thin-walled cyst (A) within the lesser sac; which demonstrates mild uniform wall enhancement (B-C) in keeping with a large pancreatic pseudocyst. The central drop of signal on (A) is related to dielectric shading artifact.
- Citation: Busireddy KK, AlObaidy M, Ramalho M, Kalubowila J, Baodong L, Santagostino I, Semelka RC. Pancreatitis-imaging approach. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014; 5(3): 252-270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v5/i3/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.252