Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2014; 5(3): 252-270
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.252
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.252
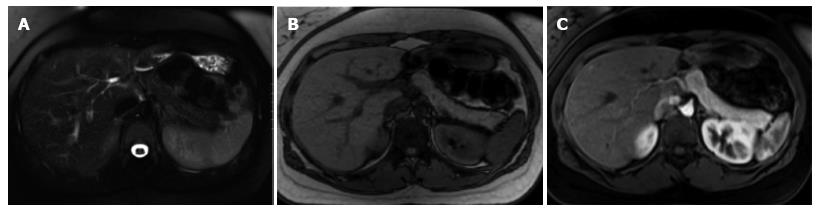
Figure 1 Normal pancreatic appearance on magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Axial T2-weighted image with fat-suppression; B: Axial GRE out-of-phase T1-weighted image; C: Axial post-contrast 3D-GRE T1-weighted image with fat-suppression during the late arterial phase. The pancreas demonstrates low T2 signal intensity (A) and high T1 signal intensity on pre-contrast images (B), reflecting high protein content of the exocrine gland. The pancreas demonstrates avid homogenous enhancement on immediate post-contrast images (C), reflecting a normal capillary blush.
- Citation: Busireddy KK, AlObaidy M, Ramalho M, Kalubowila J, Baodong L, Santagostino I, Semelka RC. Pancreatitis-imaging approach. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014; 5(3): 252-270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v5/i3/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.252