Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2014; 5(3): 188-199
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.188
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.188
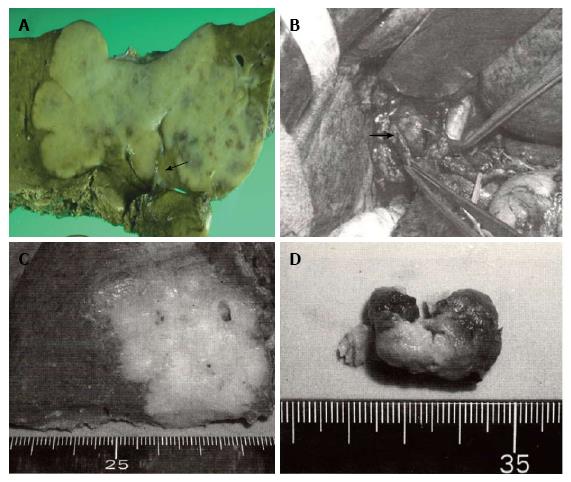
Figure 1 Some intraductal growth-type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas are considered to be an intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct, this classification system provides useful information during surgery.
A: Gross feature of mass-forming (MF) + periductal infiltrating (PI)-type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) obtained by left hepatectomy with bile duct resection. The carcinoma spreads along the hilar biliary tree (arrow) in communication with a white firm mass; B-D: Operative findings and resected specimens of MF + intraductal growth (IG)-type ICC. The common hepatic duct is incised, and the soft tumor comprising the intraductal components is easily removed (arrow) without infiltration to the ductal wall; C: Hepatic anterior segmentectomy is performed for MF components; D: IG components are composed of tan-colored soft tissues with necrosis.
- Citation: Sanada Y, Kawashita Y, Okada S, Azuma T, Matsuo S. Review to better understand the macroscopic subtypes and histogenesis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014; 5(3): 188-199
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v5/i3/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.188