Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Feb 15, 2013; 4(1): 1-11
Published online Feb 15, 2013. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v4.i1.1
Published online Feb 15, 2013. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v4.i1.1
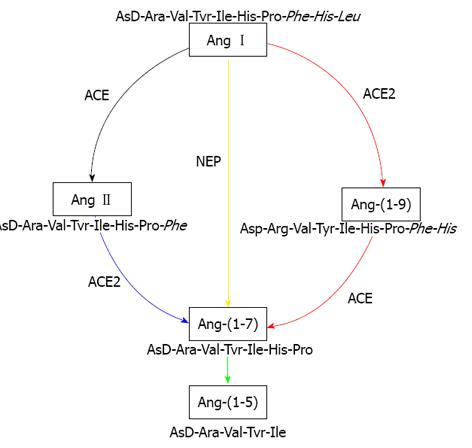
Figure 2 Intrahepatic enzymatic pathways of renin angiotensin system peptide production.
Schematic representation of the pathways responsible for the generation of vasodilator peptide angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] in rat liver. The colour of the arrows represents the relative contribution of each pathway for ex vivo formation of Ang-(1-7) from the substrates angiotensin I (Ang I) and angiotensin II (Ang II) in cirrhotic rat liver. The most efficient pathway is represented by blue line, followed by green line. The black line is the least efficient pathway whilst red represents the efficiency less than green but higher than black. The yellow colour represents an efficient pathway to generate Ang-(1-7) directly from Ang I by the action of neutral endopeptidase (NEP) but it appears that this pathway is masked by angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in cirrhotic rat liver. Ang-(1-9): Angiotensin-(1-9); Ang-(1-5): Angiotensin-(1-5); ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; NEP: Neutral endopeptidase. Figure was adapted from our previous publication.
- Citation: Herath CB, Grace JA, Angus PW. Therapeutic potential of targeting the renin angiotensin system in portal hypertension. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2013; 4(1): 1-11
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v4/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v4.i1.1