Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Feb 15, 2013; 4(1): 1-11
Published online Feb 15, 2013. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v4.i1.1
Published online Feb 15, 2013. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v4.i1.1
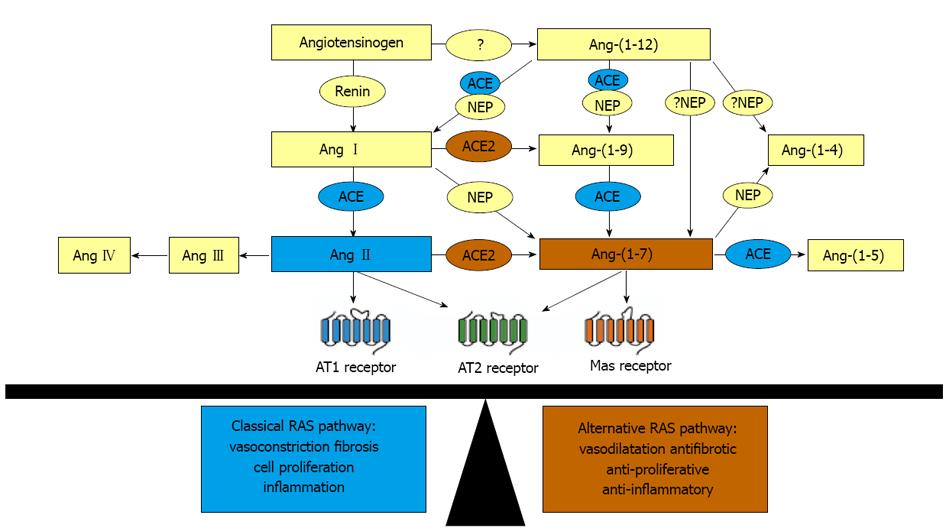
Figure 1 Overview of the renin angiotensin system.
The effects of the renin angiotensin system (RAS) are determined by the balance between the angiotensin II (Ang II)-mediated “classical” axis, depicted in blue, which is vasoconstrictive and the angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)]-mediated “alternate” axis, depicted in orange, which is vasodilatory. Both Ang II and Ang-(1-7) can stimulate the Ang II type 2 (AT2) receptor, depicted in green; the effects of which are often analogous to those mediated by the Ang-(1-7) receptor Mas. Recent evidence indicates that a new member, Ang-(1-12), which is cleaved from angiotensinogen, also contributes either indirectly via Ang I or directly to the pool of Ang-(1-7). NEP: Neural endopeptidase; ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; AT1 receptor: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor.
- Citation: Herath CB, Grace JA, Angus PW. Therapeutic potential of targeting the renin angiotensin system in portal hypertension. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2013; 4(1): 1-11
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v4/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v4.i1.1