Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 22, 2024; 15(4): 93606
Published online Aug 22, 2024. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v15.i4.93606
Published online Aug 22, 2024. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v15.i4.93606
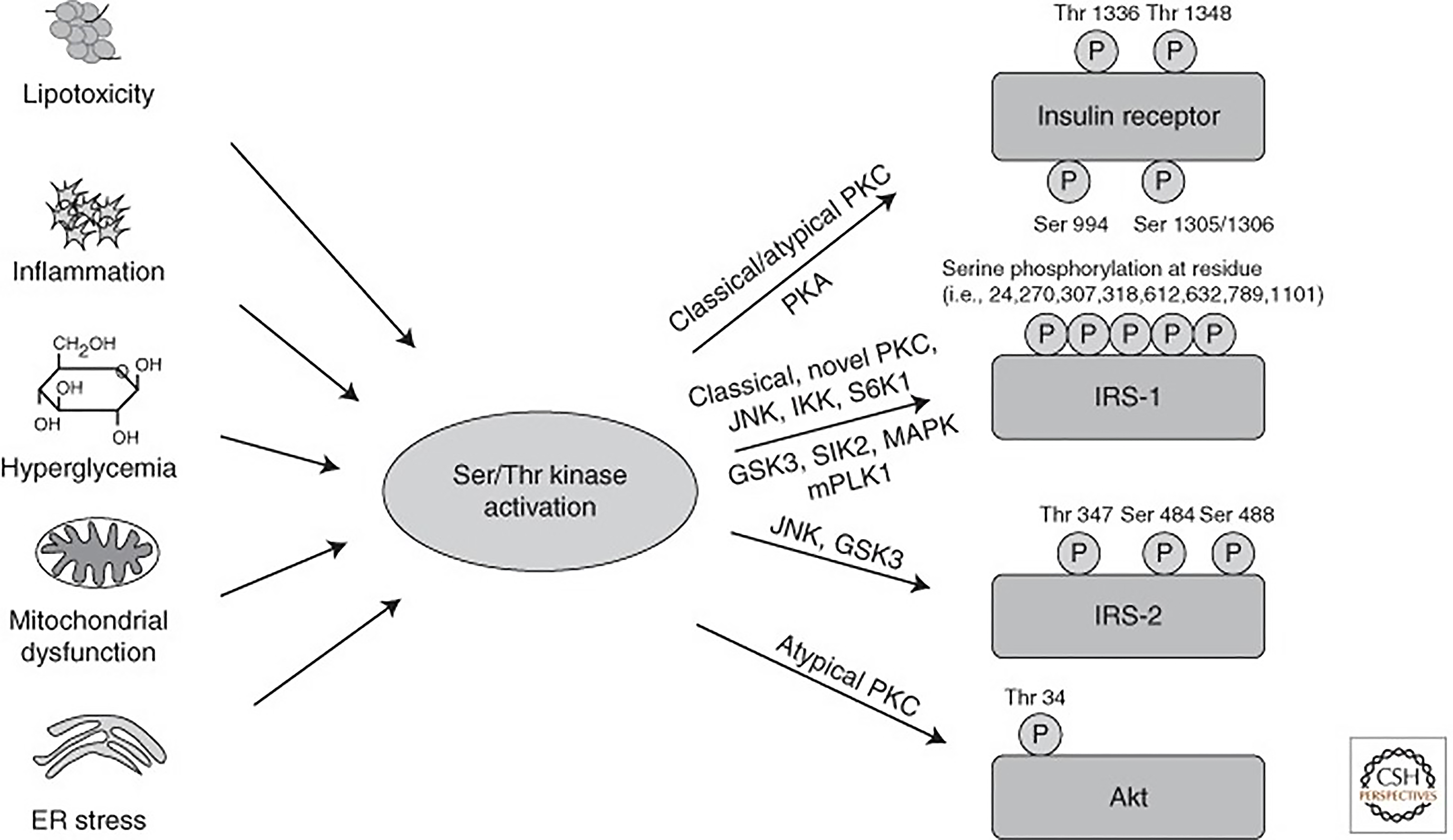
Figure 4 Activation of Ser/Thr kinases causes inhibitory phosphorylation on insulin-signaling molecules[35].
Lipotoxicity, inflammation, hyperglycemia, and subsequently oxidative stress, as well as mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress, all converge on activation of Ser/Thr kinases, inducing inhibitory Ser/Thr phosphorylation of insulin receptor, insulin receptor substrate proteins, and Akt on multiple residues, causing insulin resistance. PKC: Protein kinase C; PKA: Protein kinase A; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; IKK: Inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase; GSK: Glycogen synthase kinase 3. Citation: Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2014; 6. Copyright © The Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press 2014. Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
- Citation: Habib S. Team players in the pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunctions-associated steatotic liver disease: The basis of development of pharmacotherapy. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2024; 15(4): 93606
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v15/i4/93606.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v15.i4.93606