Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 24, 2023; 14(4): 71-85
Published online Aug 24, 2023. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v14.i4.71
Published online Aug 24, 2023. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v14.i4.71
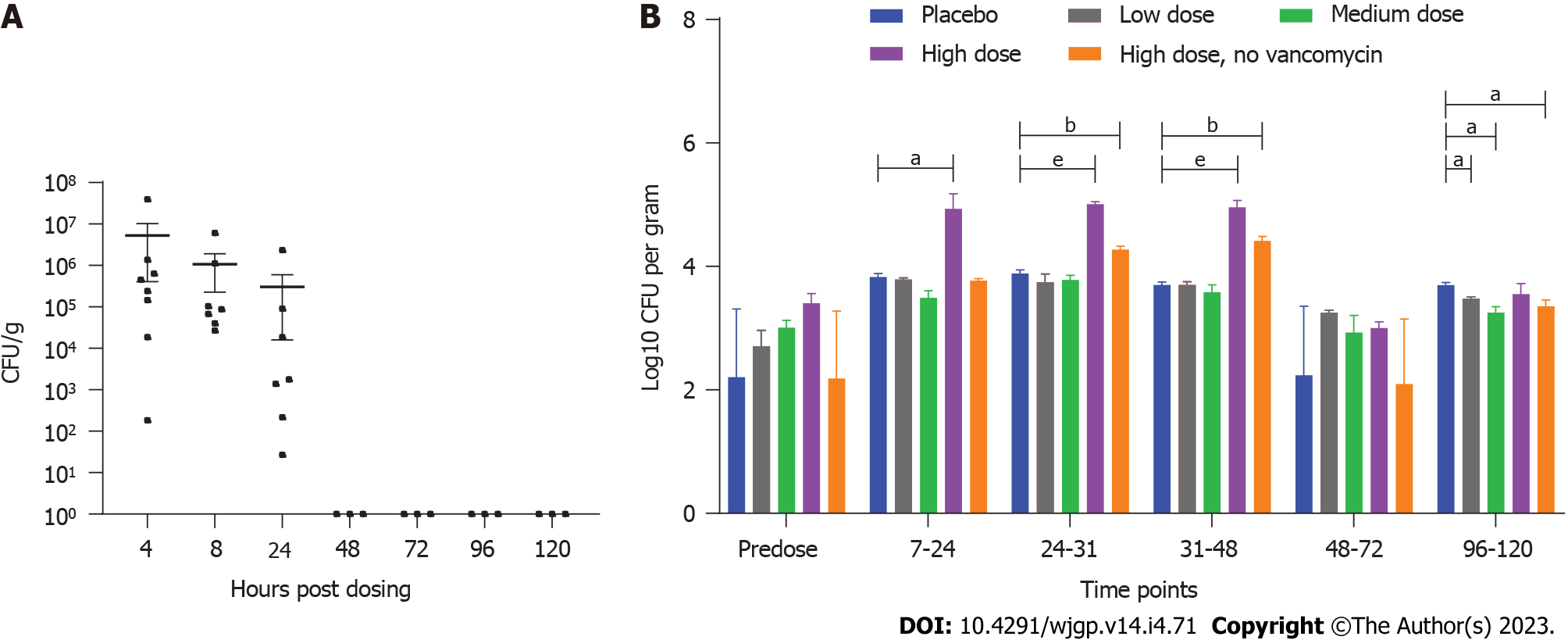
Figure 1 Quantification of ADS024 (fresh culture) in the mice and miniature swine fecal samples for the single-dose study.
A: The mice were predosed with vancomycin to mimic disruption of gut microbiota and administered a single oral dose of 5 × 108 colony-forming units (CFU)/mouse of ADS024. Microbiological analysis was subsequently conducted on the mouse fecal pellets and gastrointestinal tissue. The ADS024 colonies were recovered in feces following plating on agar media at 4 h, 8 h, and 24-h post dose; B: The single-dose study in miniature swine included 3 groups predosed with vancomycin to induce disruption of gut microbiota. They were exposed to the following dose range of ADS024: Group 2 (low dose) 6.2 × 107 CFU; Group 3 (medium dose) 7.1 × 108 CFU; and Group 4 (high dose) 7.1 × 109 CFU. There was 1 group not pre-dosed with vancomycin but exposed to a single dose of ADS024: Group 5 (no vancomycin, high dose) 7.1 × 109 CFU. The control group (Group 1, placebo) did not receive vancomycin or ADS024. After single oral administration of ADS024 to the miniature swine, the ADS024 colonies, assessed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), were detected on agar plates in the ADS024-treated Groups 4 and 5, regardless of vancomycin therapy, at colony counts higher than placebo controls that displayed only Bacillus-like colonies and not ADS024-specific ones based on qPCR, at the 7-h to 48-h time points. P value significance: aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, eP ≤ 0.001.
- Citation: Murphy CK, O’Donnell MM, Hegarty JW, Schulz S, Hill C, Ross RP, Rea MC, Farquhar R, Chesnel L. Novel, non-colonizing, single-strain live biotherapeutic product ADS024 protects against Clostridioides difficile infection challenge in vivo. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2023; 14(4): 71-85
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v14/i4/71.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v14.i4.71