Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 22, 2021; 12(6): 115-133
Published online Nov 22, 2021. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v12.i6.115
Published online Nov 22, 2021. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v12.i6.115
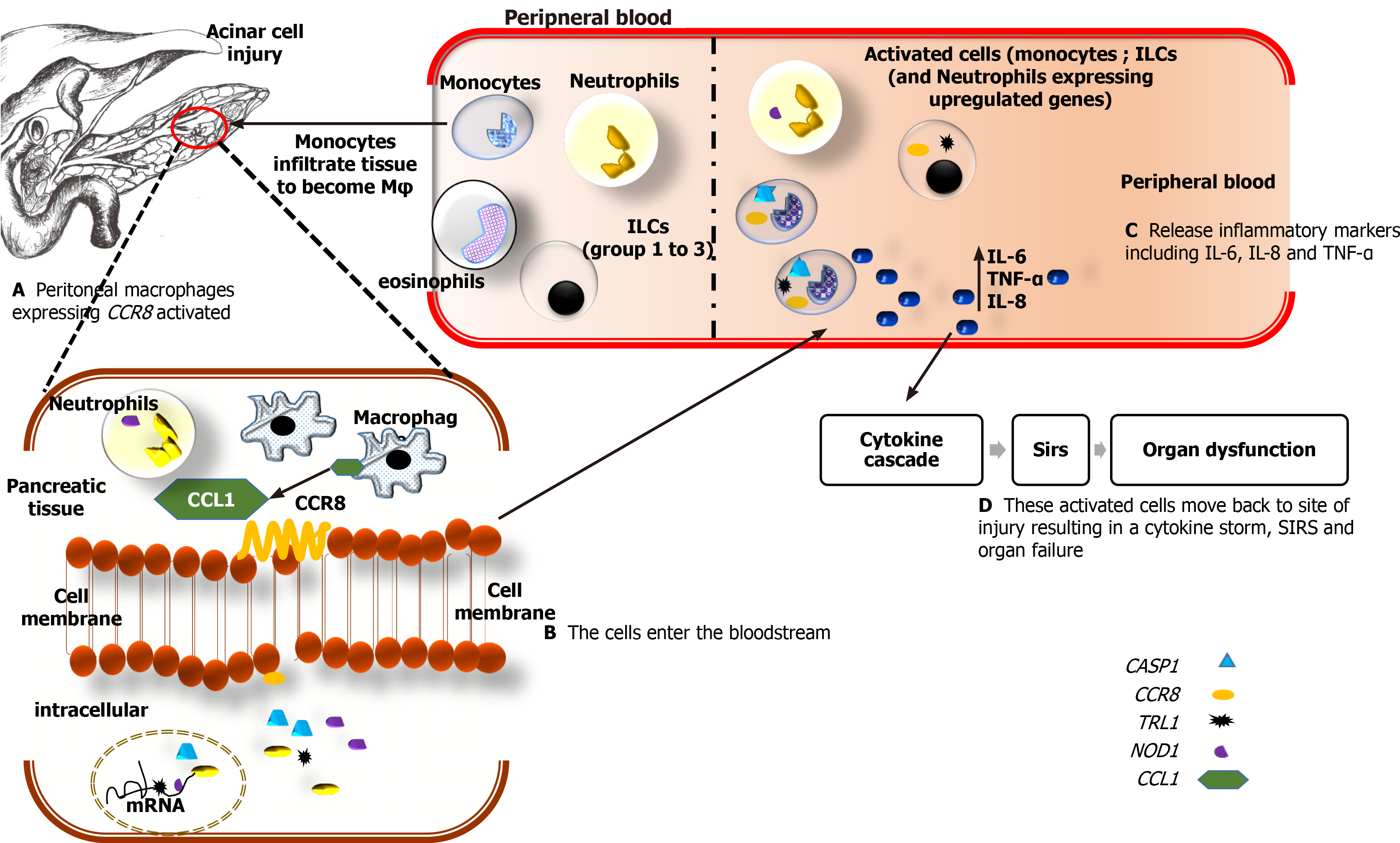
Figure 7 The schematic shows the possible mechanism by which chemokine receptor 8 is upregulated in peripheral blood.
A: Upon elevation of trypsin in the pancreas due to acinar cell injury in patients with acute pancreatitis, monocytes, lymphoid cell groups (ILCs), neutrophils and eosinophils migrate to the site of injury. Once in the pancreatic tissue, the monocytes become activated to macrophages (φ) which then express the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1 (CCL1) gene. The CCL1 binds in turn binds to the chemokine receptor 8 (CCR8) receptor on the surface of macrophages, ILC2 cells, and neutrophils. In patients with MSAP, ILC2 related cytokines, interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5, and IL-13 are upregulated while downregulation of these cytokines was observed in SAP patients (Supplementary Table 3). The observed increases in CCR8 in the SAP patients may be due to excessive activation of macrophages and monocytes. The activated cells (ILCs, neutrophils, monocytes) may be releasing IL-1-β, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), IL-6 at local sites, which send signals that activate and recruit inflammatory cells which include macrophages, neutrophils, ILC2, and ILC3; B-D: These cells migrate into the bloodstream and will express Toll-like receptor 1, Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, caspase 1 genes. These genes are mainly expressed on monocytes that will release proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α and, depending on their levels in the peripheral blood, will cause dysregulation that leads to a systemic inflammatory response and consequently single or multiple organ failure. IL: Interleukin; CASP1: Caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase; CCR8: Chemokine receptor 8; TRL1: Toll-like receptor-1; NOD1: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1; CCL1: Chemokine ligand 1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
- Citation: Nalisa M, Nweke EE, Smith MD, Omoshoro-Jones J, Devar JW, Metzger R, Augustine TN, Fru PN. Chemokine receptor 8 expression may be linked to disease severity and elevated interleukin 6 secretion in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2021; 12(6): 115-133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v12/i6/115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v12.i6.115