Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 22, 2021; 12(6): 115-133
Published online Nov 22, 2021. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v12.i6.115
Published online Nov 22, 2021. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v12.i6.115
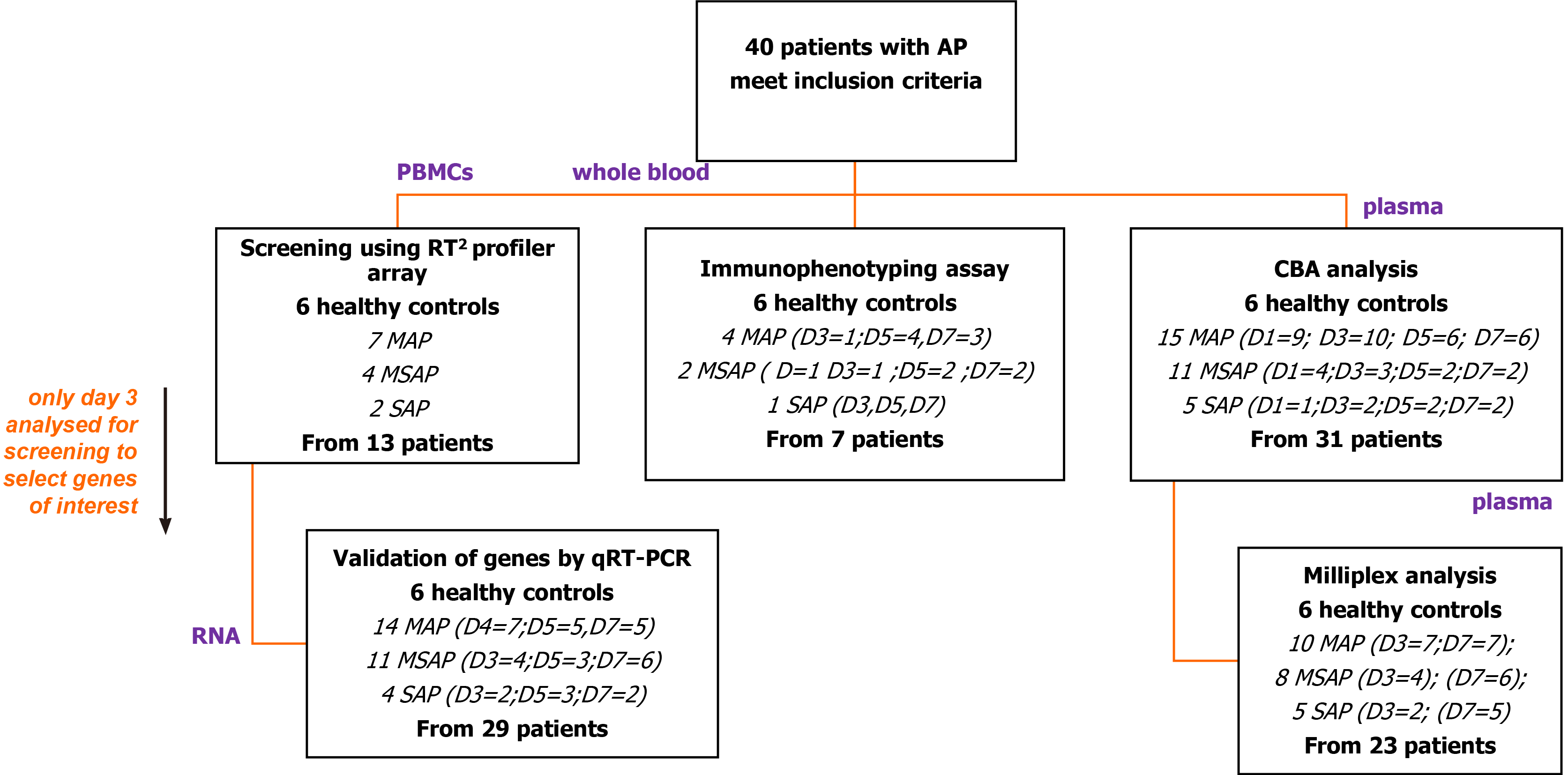
Figure 1 Flow diagram of patient recruitment.
From the 40 patients and 6 healthy controls recruited over the study period, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, whole blood and plasma were used for the various study assays as shown. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 13 patients with Day 3 data were used to do a screening study of innate and adaptive immune cell genes using RT2 Profiler Array (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). CCR8 was selected as a target gene and further verification studies done in 29 patients as depicted. For immunophenotyping, 12 antibodies were selected to discriminate monocytes, lymphocytes, and granulocytes and their subpopulations from blood samples of seven patients. An exploratory study of seven Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokines was done on 31 patient samples and 23 of these randomly selected for further analysis using the MILLIPLEX® assay. PBMCs: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; RT2: Reverse transcriptase square; D: Day; MAP: Mild acute pancreatitis; MSAP: Moderately severe acute pancreatitis; SAP: Severe acute pancreatitis; CCR8: Chemokine receptor 8; Th1/Th2/Th17: T helper type 1/2/17.
- Citation: Nalisa M, Nweke EE, Smith MD, Omoshoro-Jones J, Devar JW, Metzger R, Augustine TN, Fru PN. Chemokine receptor 8 expression may be linked to disease severity and elevated interleukin 6 secretion in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2021; 12(6): 115-133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v12/i6/115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v12.i6.115