Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Jun 15, 2010; 1(2): 63-68
Published online Jun 15, 2010. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v1.i2.63
Published online Jun 15, 2010. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v1.i2.63
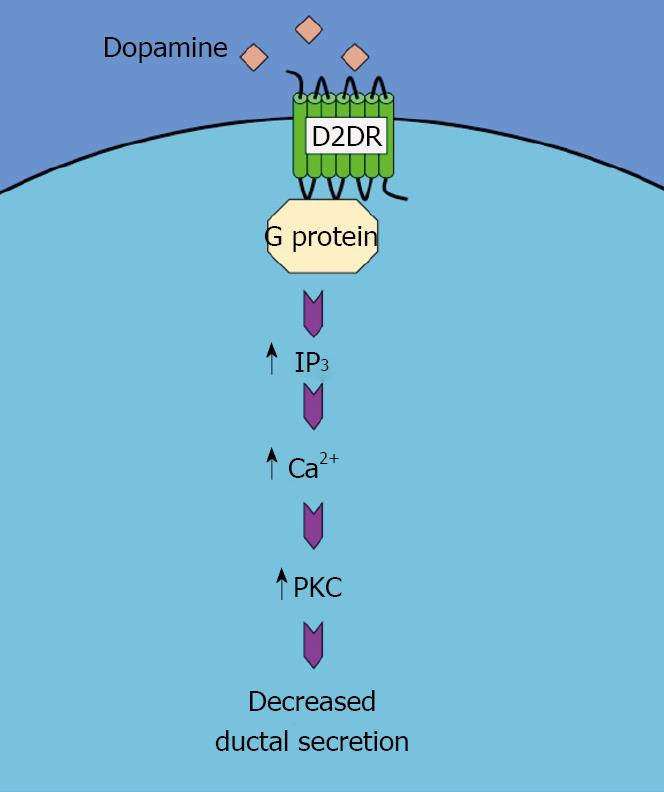
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the mechanism of the dopamine-induced decrease in ductal secretion.
Activation of D2DR results in an increase in IP3/Ca2+/PKC pathway, which in turn decreases the ductal secretion.
- Citation: Frampton GA, Li H, Ramirez J, Mohamad A, DeMorrow S. Biogenic amines serotonin and dopamine regulate cholangiocyte hyperplastic and neoplastic growth. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2010; 1(2): 63-68
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v1/i2/63.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v1.i2.63