Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Radiol. May 28, 2017; 9(5): 217-222
Published online May 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i5.217
Published online May 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i5.217
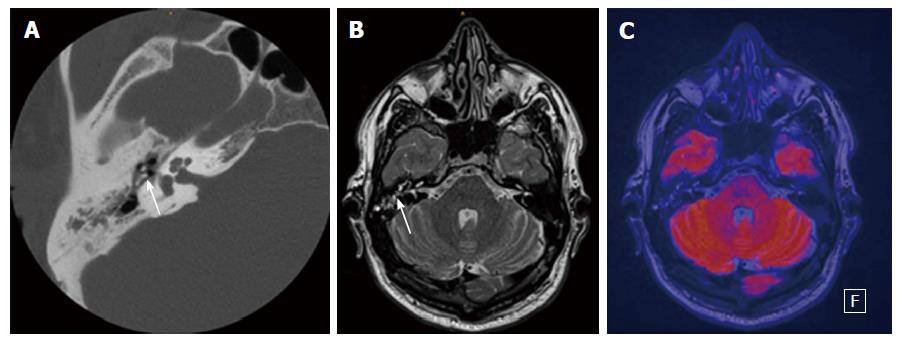
Figure 1 Thirty-nine-year-old male patient with clinically suspected cholesteatoma in the right middle ear.
A: Axial CT of the temporal bone with soft-tissue mass in the tympanic space adjacent to malleolus and incus (white arrow); B: Axial T2-weighted MR depicts fluid-like signal in the tympanic space (white arrow); C: Fused axial T2-weighted image and axial EPI DWI RESOLVE without any sign of restriction. Therefore there is no evidence of cholesteatoma; the findings are consistent with chronic otitis media. CT: Computed tomography; DWI: Diffusion weighted imaging; EPI: Echo-planar imaging; RESOLVE: Readout-segmented echo-planar.
- Citation: Henninger B, Kremser C. Diffusion weighted imaging for the detection and evaluation of cholesteatoma. World J Radiol 2017; 9(5): 217-222
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v9/i5/217.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v9.i5.217