Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2016; 8(7): 716-725
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.716
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.716
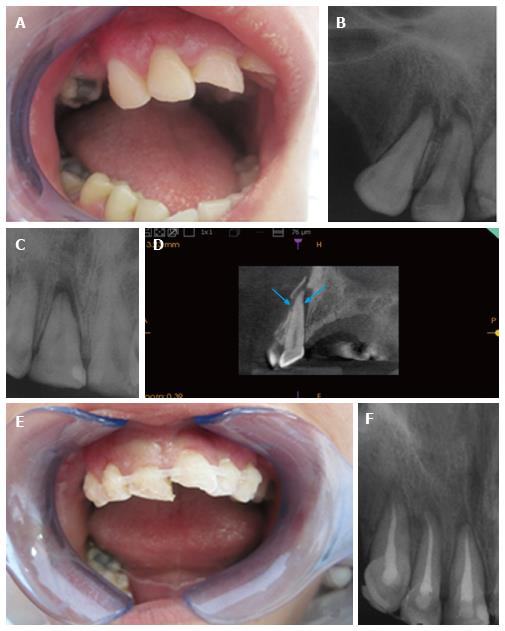
Figure 6 Clinical and radiological assessment of maxillary anterior teeth.
A: Clinical intraoral appearance of the patient; B and C: Intraoral radiographs taken from two different angels showed periapical radiolucencies in canine and incisors but they were unable to show a suspected horizontal root fracture (HRF); D: With CBCT Kodak 9000 3D (Eastman Kodak Co, Rochester, NY, United States) CMOS sensor with optical fiber, offering a single 5 cm × 3.8 cm FOV at 0.076 mm a HRF of central incisor along with alveolar bone fracture was detected in cross-sectional views; E: Intraoral appearance of the patient after splinting of canine and incisors; F:Periapical radiography showing treatment of canine and incisors with guta percha and AH Plus. CBCT: Cone beam computed tomography.
- Citation: Yılmaz F, Kamburoglu K, Yeta NY, Öztan MD. Cone beam computed tomography aided diagnosis and treatment of endodontic cases: Critical analysis. World J Radiol 2016; 8(7): 716-725
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i7/716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.716