Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2016; 8(7): 716-725
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.716
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.716
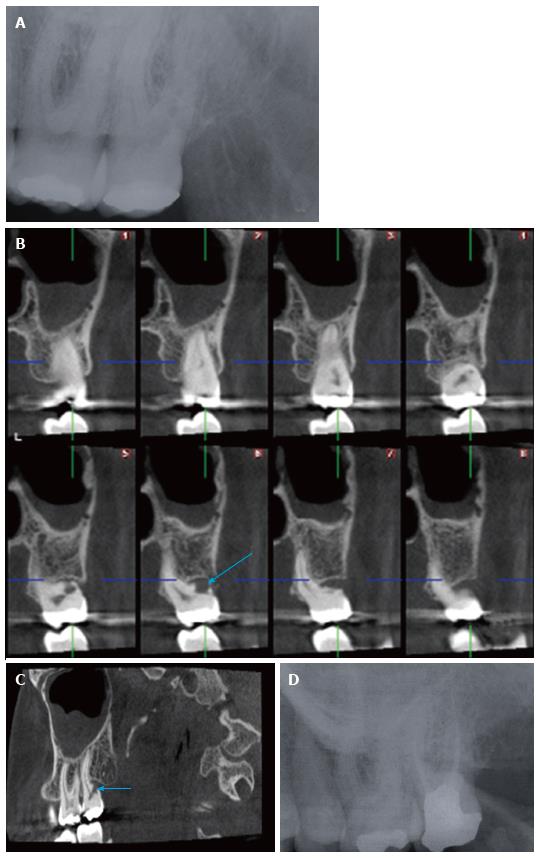
Figure 1 Radiological assessment of maxillary left second molar.
A: Periapical radiography of the left maxillary second molar tooth taken with an X-ray generator, Evolution X3000 2C/1 New Life (New Life Radiology, Grugliasco, TO, Italy) operated at 70 kVp, 8 mA and 0.3 s. using Kodak Insight F Speed Film (Kodak, Rochester, NY, United States) shows no apparent pathology; Cross sectional (B) and sagittal CBCT (C) images of the same tooth obtained by Planmeca ProMax 3D Max CBCT unit (Planmeca Oy, Helsinki, Finland) with a flat panel sensor, operating at 96 kVp, 8.0 mA, using High Definition, 0.15 mm3 voxel size, and a 55 mm × 50 mm FOV. The exposure time was 15.405 s and the DAP (mGy*cm2) value was 513 mGy*cm2. Arrows show external resorption of the buccodistal root apparently; D: Follow up periapical radiography taken 1 year after root canal treatment showed no sign of pathology. CBCT: Cone beam computed tomography; FOV: Field of view; DAP: Dose area product.
- Citation: Yılmaz F, Kamburoglu K, Yeta NY, Öztan MD. Cone beam computed tomography aided diagnosis and treatment of endodontic cases: Critical analysis. World J Radiol 2016; 8(7): 716-725
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i7/716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.716