Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Mar 28, 2016; 8(3): 268-274
Published online Mar 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i3.268
Published online Mar 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i3.268
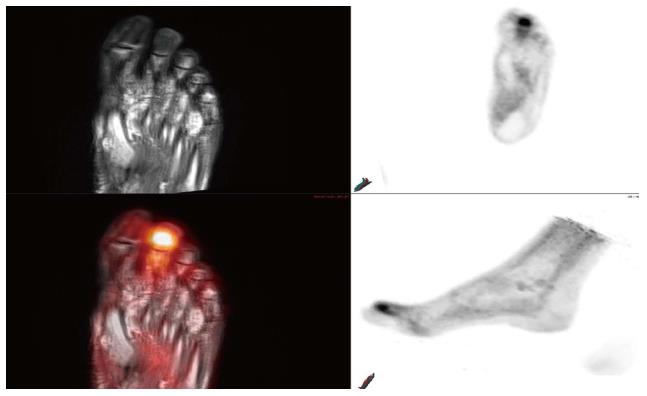
Figure 6 A 71-year-old male with poorly controlled diabetes and end-stage renal disease presents with worsening right foot pain.
Bone scan revealed diffuse radiotracer uptake within the right foot without focal abnormality. MRI of the right foot demonstrate diffuse abnormal T1 and T2 signal within the right foot digits. Multiplanar PET-MRI images reveal focal FDG uptake within the distal right second digit with corresponding heterogeneous T1 hypointense, T2 hyperintense signal compatible with osteomyelitis. PET: Positron emission tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; FDG: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose.
- Citation: Chaudhry AA, Gul M, Gould E, Teng M, Baker K, Matthews R. Utility of positron emission tomography-magnetic resonance imaging in musculoskeletal imaging. World J Radiol 2016; 8(3): 268-274
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i3/268.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i3.268