Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Jan 28, 2016; 8(1): 109-116
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i1.109
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i1.109
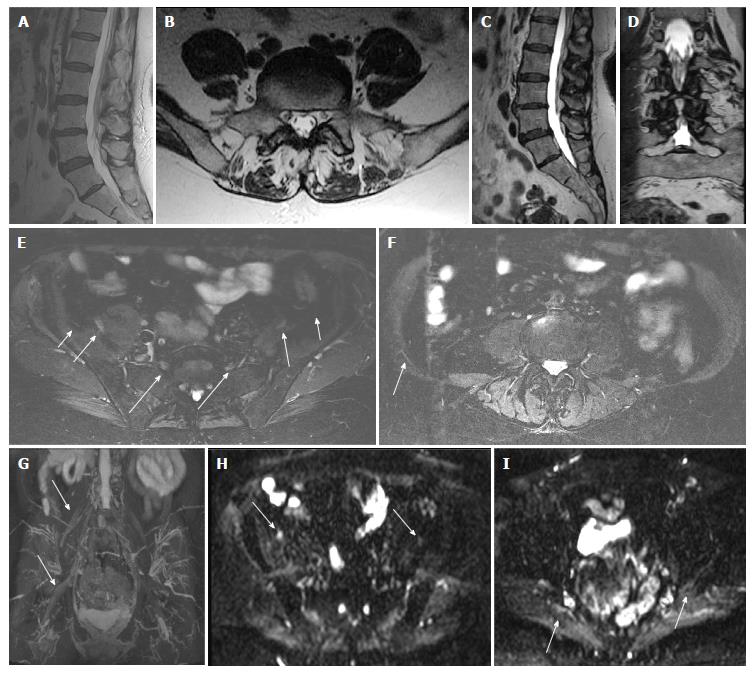
Figure 4 Right Lumbosacral plexopathy.
A 74-year-old woman with right leg and pelvic pain and mild right leg weakness. Outside LS spine MR (A and B) was reported negative. MRN LS plexus shows the transitional, partially sacralized L5 vertebra (C and D) and abnormally hyperintense right sided nerves (E), namely, lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (small arrow); femoral nerve (medium arrow), and L5 nerve (large arrow). Axial T2 SPAIR image shows hyperintense iliohypogastric nerve (arrow in F) and 3D MIP IR TSE image (G) confirms the right sided neural abnormalities. Axial DTI (H and I) images show the conspicuous abnormality of the right femoral (arrow in H) and sciatic (arrow in I) nerves. Right L4 Nerve- Mean FA = 0.46 Mean ADC = 1231 mm2/s; Left L4 Nerve- Mean FA = 0.5 Mean ADC = 1304. Right L5 Nerve-Mean FA = 0.26 Mean ADC = 1193.7 mm2/s; Left L5 Nerve-Mean FA = 0.36 Mean ADC = 1141 mm2/s. MR: Magnetic resonance; MRN: Magnetic resonance neurography; LS: Lumbosacral; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; T: Tesla; 3D: 3-Dimensional; IR: Inversion recovery; SPAIR: Spectral adiabatic inversion recovery; DTI: Diffusion tensor imaging; FA: Fractional anisotropy; ADC: Apparent diffusion coeffcient; TSE: Turbo spin echo.
- Citation: Chhabra A, Farahani SJ, Thawait GK, Wadhwa V, Belzberg AJ, Carrino JA. Incremental value of magnetic resonance neurography of Lumbosacral plexus over non-contributory lumbar spine magnetic resonance imaging in radiculopathy: A prospective study. World J Radiol 2016; 8(1): 109-116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i1/109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i1.109