Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2015; 7(12): 438-447
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438
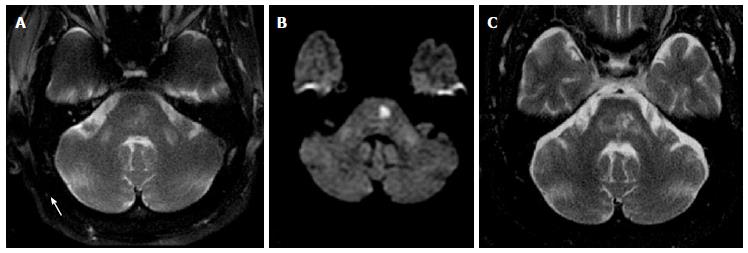
Figure 9 Wallerian degeneration of middle cerebellar peduncles.
Axial T2 (A) and DWI (B) images show symmetric areas of abnormal signal in bilateral MCP as well as focal area of restricted diffusion in the left pons (note the characteristic spare of the midline due to occlusion of para-median branches of basilar artery); Axial T2 (C), 3 years f/u, shows evolution of lacunar infarction in the pons with resolution of abnormal signal in the right MCP and persistent abnormal signal and development of volume loss in the left MCP. Findings are consistent with WD of the MCP, with “acute” early changes in the bilateral MCP and subsequent left greater than right involvement on follow up (ipsilateral to infarct). WD: Wallerian degeneration; MCP: Middle cerebellar peduncles.
- Citation: Morales H, Tomsick T. Middle cerebellar peduncles: Magnetic resonance imaging and pathophysiologic correlate. World J Radiol 2015; 7(12): 438-447
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i12/438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438