Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2015; 7(12): 424-437
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.424
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.424
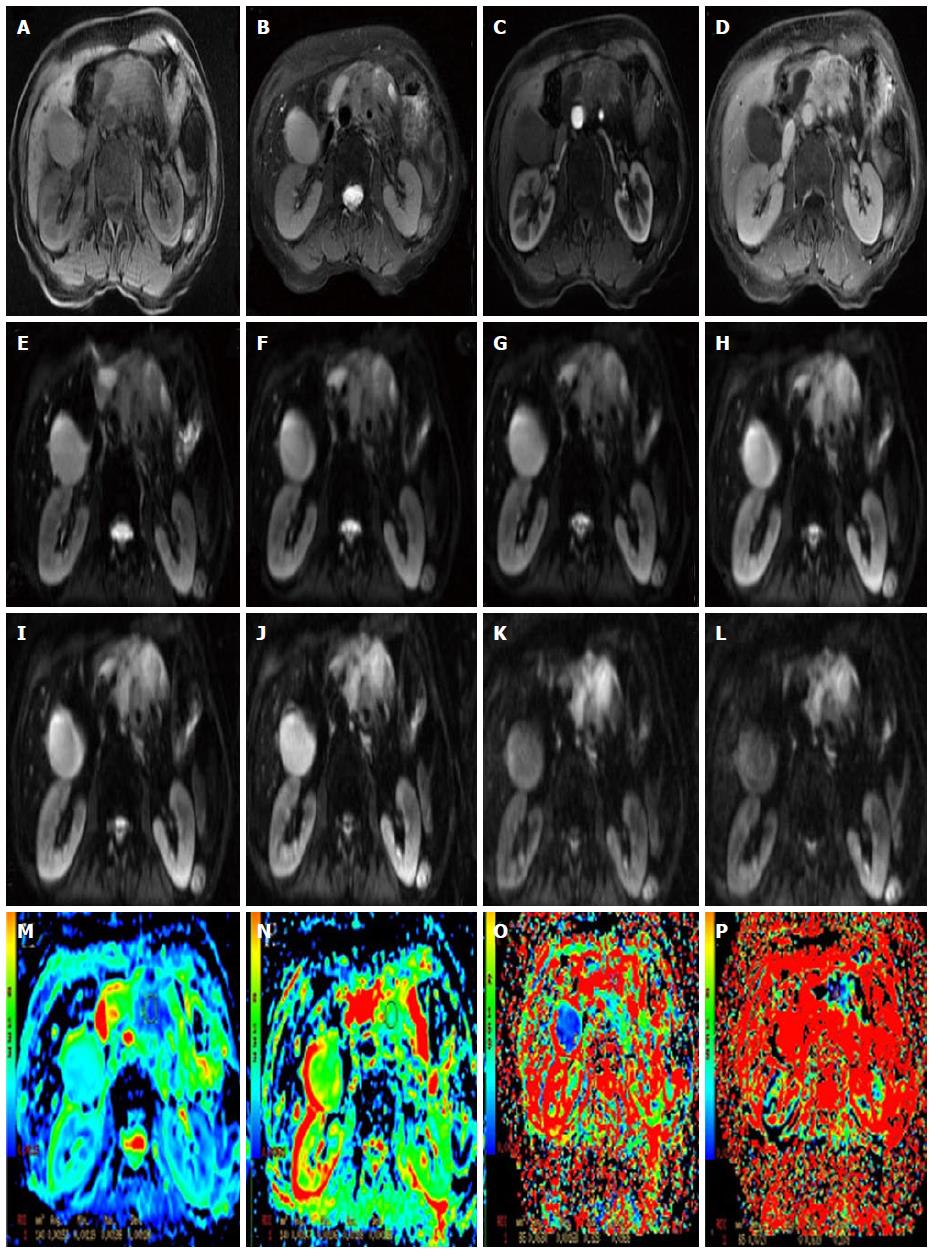
Figure 4 Images in a 65-year-old woman with a focal lesion in the neck of the pancreas.
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging suggests that it is a malignancy. A: Axial T1-weighted fat-suppressed gradient-echo MR image; B: Axial T2-weighted fat-suppressed fast spin-echo MR image; C and D: Axial slab three-dimensional liver acquisition with volume acceleration dynamic contrast-enhanced; E-L: Multi-b DWI (b = 0, 50, 100, 300, 500, 800, 1000 and 1500); M-P: Standard ADC = 1.52 × 10-3 mm2/s, slow ADC = 1.39 × 10-3 mm2/s, fast ADC = 63 × 10-3 mm2/s and f = 7.2% generated by the post-processing from the multi-b DWI. DWI: Diffusion weighted imaging; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient.
- Citation: Tang MY, Zhang XM, Chen TW, Huang XH. Various diffusion magnetic resonance imaging techniques for pancreatic cancer. World J Radiol 2015; 7(12): 424-437
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i12/424.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.424