Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2015; 7(11): 361-374
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.361
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.361
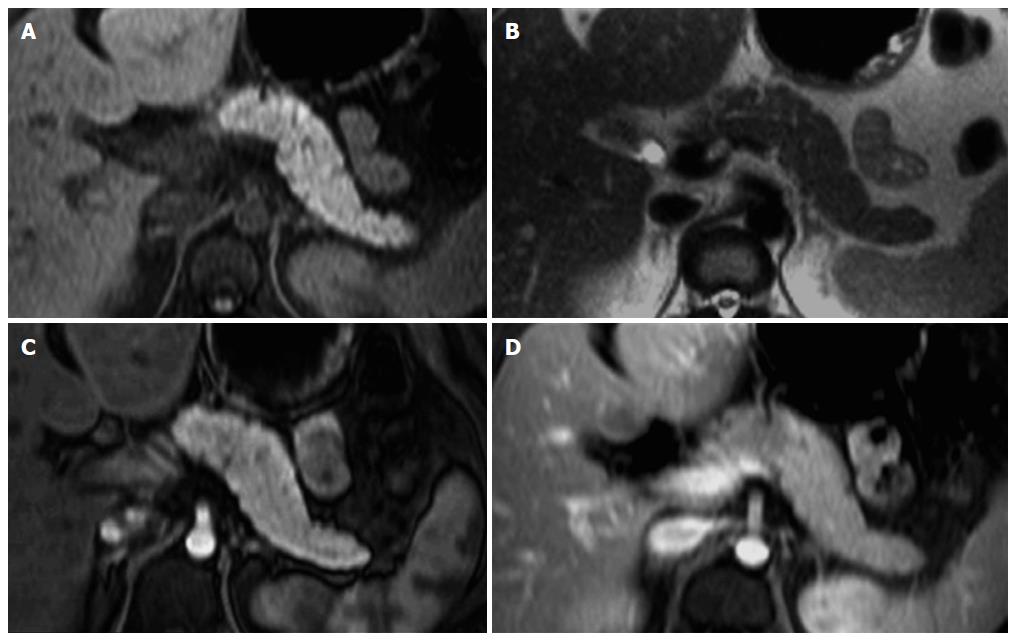
Figure 1 Normal pancreas.
Axial T2-weighted SS-ETSE (A), pre-contrast fat-suppressed T1-weighted (B) GRE and post-gadolinium fat-suppressed T1-weighted gradient echo images acquired in the arterial (C) and venous (D) phases of enhancement. The normal pancreas is high in signal intensity on T1-weighted images (B) due to the presence of aqueous protein in the pancreatic acini. A uniform capillary blush is apparent on the immediate post-gadolinium image (C). T2-weighted sequences allow the depiction of the pancreatic duct. SS-ETSE: Single-shot echo train spin echo; GRE: Gradient echo.
- Citation: Al Ansari N, Ramalho M, Semelka RC, Buonocore V, Gigli S, Maccioni F. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the detection and characterization of solid pancreatic nodules: An update. World J Radiol 2015; 7(11): 361-374
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i11/361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.361