Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2014; 6(8): 625-628
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.625
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.625
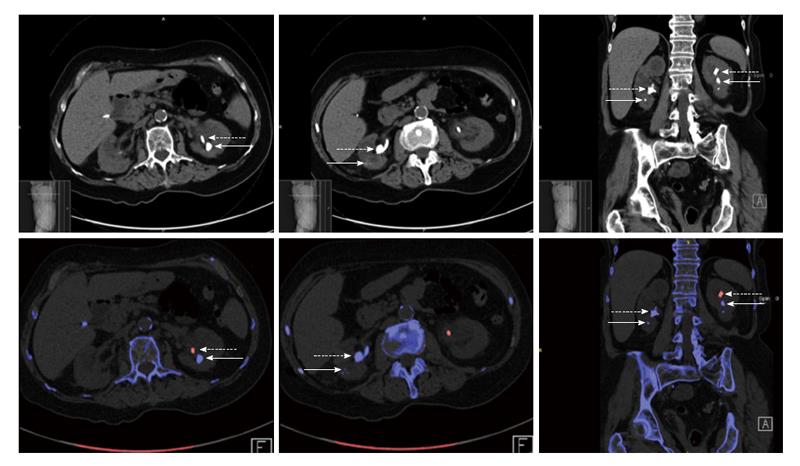
Figure 1 Conventional and dual-energy computed tomography images of kidney stones and ureteral stents.
Conventional computed tomography (top) and dual-energy computed-tomography (DECT, bottom) images showing the advantage of DECT for stone visualization and identification of composition. The solid and dashed arrows point to stones and stents, respectively. The different stent and stone colors in the left kidney enhanced stone visualization, while the visualization of the stone in the right kidney is compromised because it has the same color as the stent. The small cubes in the bottom show the view orientation in the 3D [Anterior (A); and Foot (F)].
- Citation: Ibrahim ESH, Haley WE, Jepperson MA, Wehle MJ, Cernigliaro JG. Characterization of ureteral stents by dual-energy computed tomography: Clinical implications. World J Radiol 2014; 6(8): 625-628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i8/625.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.625