Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2014; 6(8): 544-566
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.544
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.544
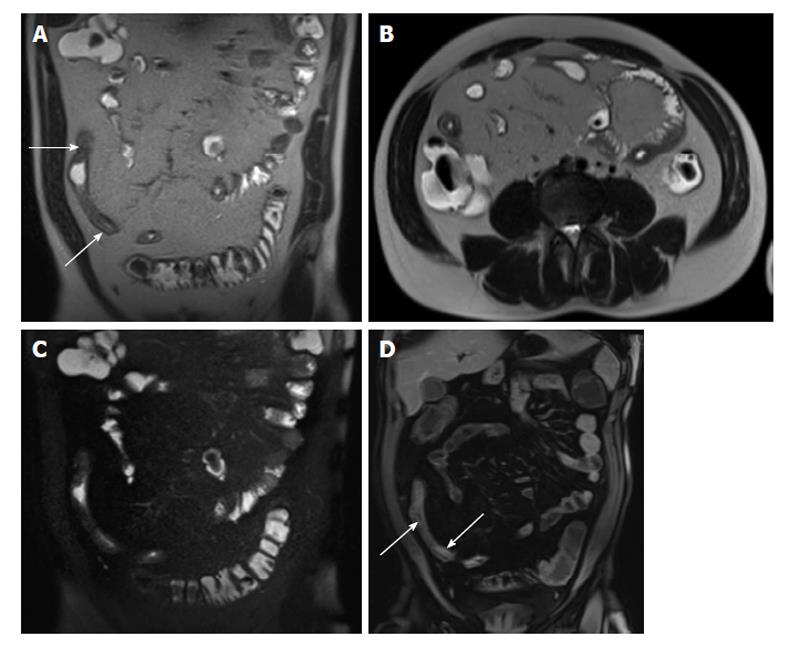
Figure 7 Acute on chronic Crohn’s disease.
A: Coronal and (B) axial T2-weighted single shot fast spin echo (SSFSE) as well as (C) coronal fat-suppressed T2-weighted SSFSE and (D) coronal fat-suppressed interstitial post-gadolinium 3D-GRE T1-weighted images during the interstitial phase. There is distal small bowel segment which demonstrates diffuse thickening and luminal narrowing (arrows, A), associated with submucosal high signal intensity on T2-weighted images (A and B) and with low-signal intensity on the fat-suppressed T2-weighted images (C), related to submucosal fat deposition, in keeping with chronic Crohn’s disease. There is also a superimposed increased mucosal enhancement in affected bowel segments (arrows, D) and comb sign post-gadolinium images (D), reflecting disease activity, in keeping with acute on top of chronic disease. GRE: Gradient recalled echo.
- Citation: Liu B, Ramalho M, AlObaidy M, Busireddy KK, Altun E, Kalubowila J, Semelka RC. Gastrointestinal imaging-practical magnetic resonance imaging approach. World J Radiol 2014; 6(8): 544-566
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i8/544.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.544