Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2014; 6(8): 530-537
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.530
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.530
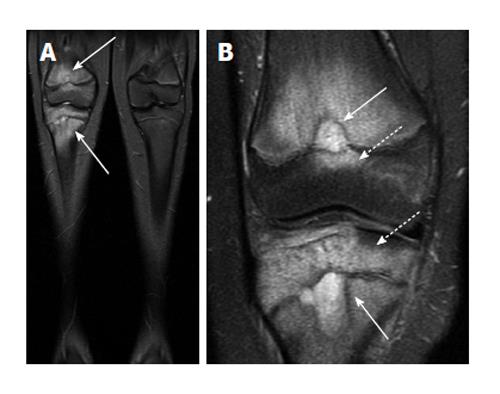
Figure 11 Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis.
A: Coronal short-tau inversion recovery image from whole body magnetic resonance imaging (lower extremity station) shows areas of bone marrow edema in the distal femur and proximal tibia; B: Coronal T2-weighted fat suppressed image with smaller field of view again demonstrates the bone marrow edema as well as two areas of very hyperintense T2 signal in the femur and tibia which may represent intraosseous abscesses (solid arrows), though these are not typically found in chronic multifocal recurrent osteomyelitis. Involvement of the epiphysis is apparent at both sites (dashed arrows).
- Citation: Pugmire BS, Shailam R, Gee MS. Role of MRI in the diagnosis and treatment of osteomyelitis in pediatric patients. World J Radiol 2014; 6(8): 530-537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i8/530.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.530