Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2014; 6(6): 313-328
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.313
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.313
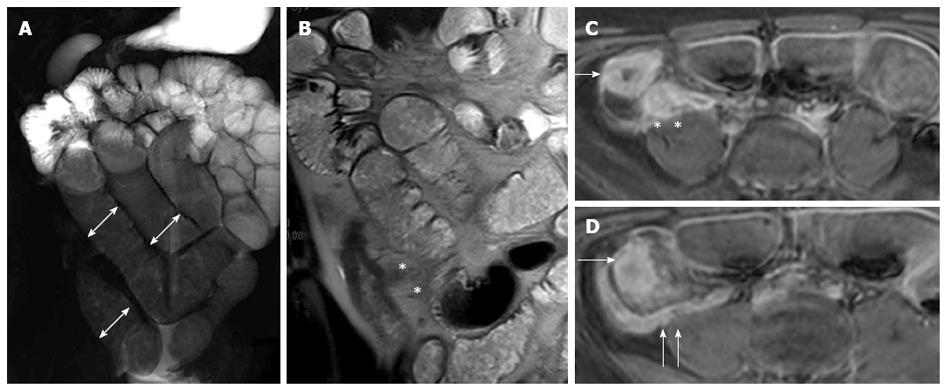
Figure 18 Fifteen years old male with small bowel obstruction caused by fibrotic stricture.
Thick-slab T2-w sequence (A) shows bowel dilatation greater than 3 cm (double arrows), according to functionally significant stricture. Coronal T2-w sequence (B) shows mural thickening of the terminal ileum without increased wall signal (asterisks). Transverse (C and D) CE FS-T1-w 3D GE show a homogeneous avidly enhancing of the cecum (arrow in C and D), terminal ileum (asterisks in C) and appendix (arrows in D). These findings can be finding in the small bowel obstruction due to fibrotic stricture.
- Citation: Casciani E, Vincentiis CD, Polettini E, Masselli G, Nardo GD, Civitelli F, Cucchiara S, Gualdi GF. Imaging of the small bowel: Crohn’s disease in paediatric patients. World J Radiol 2014; 6(6): 313-328
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i6/313.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.313