Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Apr 28, 2014; 6(4): 106-115
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i4.106
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i4.106
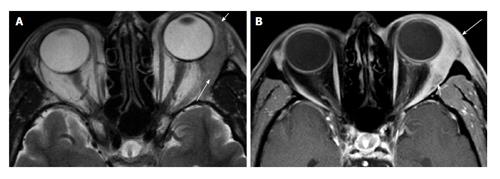
Figure 1 Dacryoadenitis.
A: Axial T2 shows diffuse enlargement of the left lacrimal gland. Note the tapered posterior margin (long arrow), as well as the involvement of the orbital lobe (short arrow). These findings suggest a lymphoid or inflammatory process rather than an epithelial neoplasm; B: Axial fat-suppressed contrast-enhanced T1 shows infiltration of the preseptal (long arrow) and post septal (short arrow) fat. These features suggest orbital inflammatory disease rather than orbital lymphoma.
- Citation: Pakdaman MN, Sepahdari AR, Elkhamary SM. Orbital inflammatory disease: Pictorial review and differential diagnosis. World J Radiol 2014; 6(4): 106-115
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i4/106.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i4.106