Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
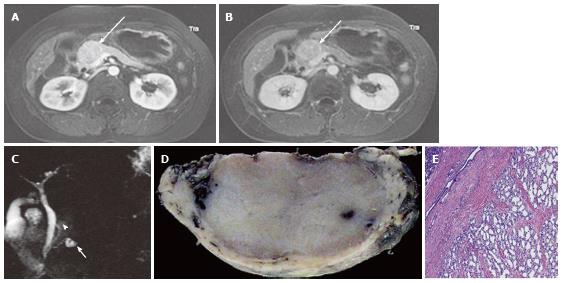
Figure 3 A 43-year-old female with solid-appearing serous cystic neoplasm in the pancreatic head.
A: The arterial phase of an axial contrast enhanced (CE) T1-weighted gradient-echo (GRE) magnetic resonance (MR) image with fat saturation shows an enhancing mass in the pancreatic head (arrow); B: The equilibrium phase of an axial CE T1-weighted GRE MR imaging shows the tumor (arrow) to be low intensity (wash-out); C: The pancreatic head mass (arrowhead) is not clearly demonstrated on MR cholangiopancreatography. The pancreatic head mass appears radiologically solid (solid-appearing). An arrow shows a concomitant small intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; D: Macroscopic view of the resected specimen shows the mass appears solid; E: Microscopic view shows the tumor consisting of small cystic structures with intervening fibrous stroma.
- Citation: Ishigami K, Nishie A, Asayama Y, Ushijima Y, Takayama Y, Fujita N, Takahata S, Ohtsuka T, Ito T, Igarashi H, Ikari S, Metz CM, Honda H. Imaging pitfalls of pancreatic serous cystic neoplasm and its potential mimickers. World J Radiol 2014; 6(3): 36-47
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i3/36.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i3.36