Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2014; 6(12): 895-906
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i12.895
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i12.895
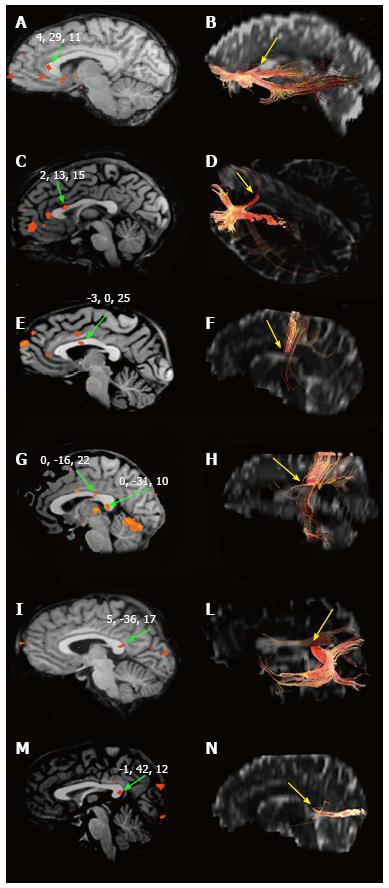
Figure 2 Blood-oxygen-level dependent effect within the corpus callosum and interhemispheric fibers.
Blood-oxygen-level dependent effect evoked in the CC by different kind of peripheral sensory stimulation (left) and CC sites where fibers interconnecting the cortical areas activated cross the CC (right). A and B: Focus evoked by olfactory stimulation and callosal fibers connecting primary olfactory cortices, respectively; C and D: The same for gustatory stimuli and areas; E and F: Motor task and motor cortex; G and H: Hand tactile stimulus and somatosensory cortex; I and L: Auditory stimuli and cortex; M and N: Visual stimuli and cortex. Authors’ original data. CC: Corpus callosum.
- Citation: Fabri M, Pierpaoli C, Barbaresi P, Polonara G. Functional topography of the corpus callosum investigated by DTI and fMRI. World J Radiol 2014; 6(12): 895-906
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i12/895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i12.895